The metabolic analysis of psoriasis identifies the associated metabolites while providing computational models for the monitoring of the disease
- PMID: 28695330
- PMCID: PMC5577063
- DOI: 10.1007/s00403-017-1760-1
The metabolic analysis of psoriasis identifies the associated metabolites while providing computational models for the monitoring of the disease
Abstract
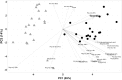
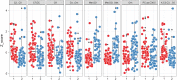
The majority of studies on psoriasis have focused on explaining the genetic background and its associations with the immune system's response. The aim of this study was to identify the low-molecular weight compounds contributing to the metabolomic profile of psoriasis and to provide computational models that help with the classification and monitoring of the severity of the disease. We compared the results from targeted and untargeted analyses of patients' serums with plaque psoriasis to controls. The main differences were found in the concentrations of acylcarnitines, phosphatidylcholines, amino acids, urea, phytol, and 1,11-undecanedicarboxylic acid. The data from the targeted analysis were used to build classification models for psoriasis. The results from this study provide an overview of the metabolomic serum profile of psoriasis along with promising statistical models for the monitoring of the disease.
Keywords: Computational model; Metabolomics; Psoriasis; Targeted analysis; Untargeted analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Tartu. Permission number 245/M-18. The Declaration of Helsinki protocols were followed and patients gave their informed, written consent.
Figures

References
-
- Abdullah MN, Yap BW, Zakaria Y, Abdul Majeed AB (2016) Metabolites selection and classification of metabolomics data on Alzheimer’s disease using random forest. In: Soft computing in data science SCDS 2016 communications in computer and information science, vol 652. Springer, Singapore
-
- Abeyakirthi S, Mowbray M, Bredenkamp N, van Overloop L, Declercq L, Davis PJ, Matsui MS, Weller RB. Arginase is overactive in psoriatic skin. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:193–196. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

