A systematic review of reviews: exploring the relationship between obesity, weight loss and health-related quality of life
- PMID: 28695722
- PMCID: PMC5600094
- DOI: 10.1111/cob.12203
A systematic review of reviews: exploring the relationship between obesity, weight loss and health-related quality of life
Abstract
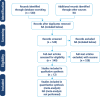
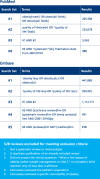
This is the first systematic review of reviews to assess the effect of obesity and weight loss on health-related quality of life (HRQoL). We identified 12 meta-analyses/systematic reviews published between January 2001 and July 2016. They addressed the following themes: (i) the relationship between weight/body mass index and HRQoL (baseline/pre-intervention; n = 2). (ii) HRQoL after weight loss (varied interventions and/or study design; n = 2). (iii) HRQoL after weight loss (randomized controlled trials only; n = 2). (iv) HRQoL after bariatric surgery (n = 6). We found that in all populations, obesity was associated with significantly lower generic and obesity-specific HRQoL. The relationship between weight loss and improved HRQoL was consistently demonstrated after bariatric surgery, perhaps due to a greater than average weight loss compared with other treatments. Improved HRQoL was evident after non-surgical weight loss, but was not consistently demonstrated, even in randomized controlled trials. This inconsistency may be attributed to variation in quality of reporting, assessment measures, study populations and weight-loss interventions. We recommend longer-term studies, using both generic and obesity-specific measures, which go beyond HRQoL in isolation to exploring mediators of HRQoL changes and interactions with other variables, such as comorbidities, fitness level and body image.
Keywords: Obesity; quality of life; weight loss; weight management.
© 2017 The Authors. Clinical Obesity published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of World Obesity Federation.
Figures

References
-
- Adams KF, Schatzkin A, Harris TB et al Overweight, obesity, and mortality in a large prospective cohort of persons 50 to 71 years old. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 763–778. - PubMed
-
- Kurth T, Gaziano JM, Berger K et al Body mass index and the risk of stroke in men. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162: 2557–2562. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Overweight & Obesity; 2016 [WWW document]. URL https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/ (accessed 27 January 2017).
-
- Young T, Shahar E, Nieto FJ et al Predictors of sleep‐disordered breathing in community‐dwelling adults: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162: 893–900. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

