Central nervous system relapse of rhabdomyosarcoma
- PMID: 28696016
- PMCID: PMC7343338
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.26710
Central nervous system relapse of rhabdomyosarcoma
Erratum in
-
Erratum: De B, Kinnaman MD, Wexler LH, Kramer K, Wolden SL. Central nervous system relapse of rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017; https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.26710.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017 Nov;64(11). doi: 10.1002/pbc.26766. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28926690 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: The optimal management of central nervous system (CNS) relapse of rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is unclear. We examined diagnosis, management, and outcomes of patients with RMS developing CNS relapse.
Methods: Records of 23 patients diagnosed with CNS relapse between 1999 and 2016 were reviewed. Median age at presentation of CNS relapse was 15 years (range, 1-34 years). High-risk features at initial presentation were as follows: 16 alveolar patients, 13 Stage IV, and 13 with primary tumor in parameningeal locations.
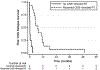
Results: CNS relapse occurred at a median 12 months (range, 1-23 months) from diagnosis and most common presenting symptoms were headache (n = 9), nausea/vomiting (n = 8), visual difficulty (n = 5), and none (n = 5). Leptomeningeal metastases were detected in 21 patients while only 2 developed parenchymal metastases without leptomeningeal involvement. Fifteen patients received CNS-directed radiation therapy (RT), including craniospinal irradiation to a median 36 Gy (range, 18-36 Gy) and/or whole brain radiotherapy to a median 30 Gy (range, 6-41.4 Gy). Three patients received concurrent chemotherapy. Follow-up magnetic resonance imaging was conducted in 13 patients after RT initiation with 8 demonstrating improvement, 2 with stable disease, and 3 with progression. Twelve patients were tested for reactivity to I-131-labeled monoclonal antibody 8H9, and three tested positive and received at least one intra-Ommaya dose; all three lived >12 months post-CNS relapse. Twenty‐two patients died of CNS disease and one of treatment complications, with metastatic disease at other sites. Median survival post-CNS relapse was 5 months (range, 0.1-49 months).
Conclusions: The prognosis for patients with RMS developing CNS relapse remains poor. Treatment including CNS-directed RT should be considered and investigation into preventative therapies is warranted.
Keywords: CNS relapse; immunotherapy; radiation therapy; rhabdomyosarcoma.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Comment in
-
Isolated central nervous system relapse of maxillary rhabdomyosarcoma presenting with neoplastic meningitis.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2018 Jul;65(7):e27029. doi: 10.1002/pbc.27029. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29512925 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gerson JM, Jaffe N, Donaldson MH Tefft M. Meningeal seeding from rhabdomyosarcoma of the head and neck with base of the skull invasion: recognition of the clinical evolution and suggestions for management. Med Pediatr Oncol 1978;5:137–144. - PubMed
-
- Yang JC, Wexler LH, Meyers PA Wolden SL. Parameningeal rhabdomyosarcoma: outcomes and opportunities. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2013;85:e61–66. - PubMed
-
- Raney RB, Meza J, Anderson JR, et al. Treatment of children and adolescents with localized parameningeal sarcoma: experience of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group protocols IRS-II through -IV, 1978–1997. Med Pediatr Oncol 2002;38:22–32. - PubMed
-
- Kline RM, Oseas RS, Jolley SG, et al. Leptomeningeal metastasis from a paraspinal rhabdomyosarcoma with a der(13)t(1;13)(q23;q32) in a 14-month-old boy. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1997;98:97–101. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources