Palladium-Catalyzed Transformations of Alkyl C-H Bonds
- PMID: 28697604
- PMCID: PMC5516964
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00622
Palladium-Catalyzed Transformations of Alkyl C-H Bonds
Abstract
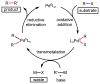
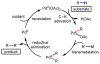
This Review summarizes the advancements in Pd-catalyzed C(sp3)-H activation via various redox manifolds, including Pd(0)/Pd(II), Pd(II)/Pd(IV), and Pd(II)/Pd(0). While few examples have been reported in the activation of alkane C-H bonds, many C(sp3)-H activation/C-C and C-heteroatom bond forming reactions have been developed by the use of directing group strategies to control regioselectivity and build structural patterns for synthetic chemistry. A number of mono- and bidentate ligands have also proven to be effective for accelerating C(sp3)-H activation directed by weakly coordinating auxiliaries, which provides great opportunities to control reactivity and selectivity (including enantioselectivity) in Pd-catalyzed C-H functionalization reactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



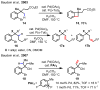
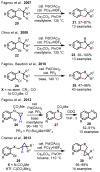
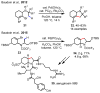
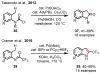



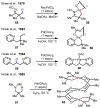
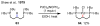
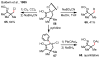
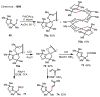


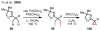
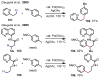
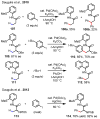
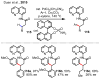






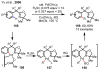

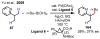
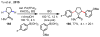




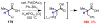


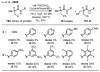
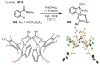

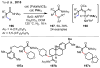
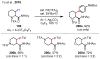


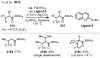


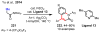

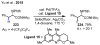
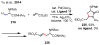



References
-
- Ryabov AD. Mechanisms of Intramolecular Activation of C–H Bonds in Transition-Metal Complexes. Chem Rev. 1990;90:403–424.
-
- Arndtsen BA, Bergman RG, Mobley TA, Peterson TH. Selective Intermolecular Carbon–Hydrogen Bond Activation by Synthetic Metal Complexes in Homogeneous Solution. Acc Chem Res. 1995;28:154–162.
-
- Shilov AE, Shul’pin GB. Activation of C–H Bonds by Metal Complexes. Chem Rev. 1997;97:2879–2932. - PubMed
-
- Kakiuchi F, Murai S. Catalytic C–H/Olefin Coupling. Acc Chem Res. 2002;35:826–834. - PubMed
-
- Ritleng V, Sirlin C, Pfeffer M. Ru-, Rh-, and Pd-Catalyzed C–C Bond Formation Involving C–H Activation and Addition on Unsaturated Substrates: Reactions and Mechanistic Aspects. Chem Rev. 2002;102:1731–1770. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

