Evaluation of the safety and efficiency of novel metallic implant scaler tips manufactured by the powder injection molding technique
- PMID: 28697771
- PMCID: PMC5504980
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-017-0396-z
Evaluation of the safety and efficiency of novel metallic implant scaler tips manufactured by the powder injection molding technique
Abstract
Background: Although many studies have compared the properties of ultrasonic scaling instruments, it remains controversial as to which is most suitable for implant scaling. This study evaluated the safety and efficiency of novel metallic ultrasonic scaler tips made by the powder injection molding (PIM) technique on titanium surfaces.
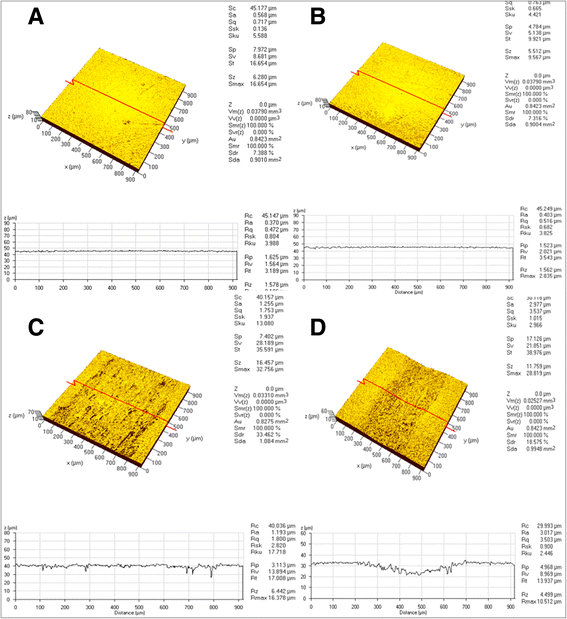
Methods: Mechanical instrumentation was carried out using four types of metal scaler tips consisting of copper (CU), bronze (BR), 316 L stainless steel (316 L), and conventional stainless steel (SS) tips. The instrumented surface alteration image of samples was viewed with scanning electron microscope (SEM) and surface profile of the each sample was investigated with confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). Arithmetic mean roughness (Ra) and maximum height roughness (Rmax) of titanium samples were measured and dissipated power of the scaler tip was estimated for scaling efficiency.
Results: The average Ra values caused by the 316 L and SS tip were about two times higher than those of the CU and BR tips (p < 0.05). The Rmax value showed similar results. The efficiency of the SS tip was about 3 times higher than that of CU tip, the 316 L tip is about 2.7 times higher than that of CU tip, and the BR tip is about 1.2 times higher than that of CU tip.
Conclusions: Novel metallic bronze alloy ultrasonic scaler tip minimally damages titanium surfaces, similar to copper alloy tip. Therefore, this bronze alloy scaler tip may be promising instrument for implant maintenance therapy.
Keywords: Efficiency; Implant scaler tip; Novel metal; Powder injection molding (PIM); Titanium surface.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures





References
-
- Bailey GM, Gardner JS, Day MH, Kovanda BJ. Implant surface alterations from a nonmetallic ultrasonic tip. J West Soc Periodontol Periodontal Abstr. 1998;46(3):69–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

