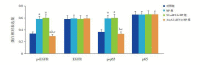[Effect of annexin A2 on EGFR/NF-κB signal transduction and mucin expression in human airway epithelial cells treated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae]
- PMID: 28697839
- PMCID: PMC7389913
- DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2017.07.018
[Effect of annexin A2 on EGFR/NF-κB signal transduction and mucin expression in human airway epithelial cells treated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of annexin A2 (AnxA2) on epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR)/nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signal transduction and mucin expression in human airway epithelial H292 cells treated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP).
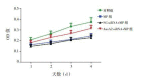
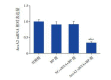
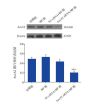
Methods: H292 cells were divided into control group, MP group, NC-siRNA+MP group, and AnxA2 siRNA+MP group. The cells in the MP group were incubated with 5 μg/mL MP antigen for 2 hours. The cells in the NC-siRNA+MP and AnxA2 siRNA+MP groups were transfected with NC-siRNA and AnxA2 siRNA for 24 hours, followed by MP antigen stimulation for 2 hours. The MTT method was used to measure cell viability; quantitative real-time PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression of AnxA2; Western blot was used to measure the protein expression of AnxA2, phosphorylated EGFR (p-EGFR), and phosphorylated p65 NF-κB (p-p65 NF-κB); ELISA was used to measure the secretion of mucin 5AC (MUC5AC) and mucin 5B (MUC5B).
Results: The MP and NC-siRNA+MP groups had lower cell viability than the control group (P<0.05). The AnxA2 siRNA+MP group had higher cell viability than the MP and NC-siRNA+MP groups and lower cell viability than the control group (P<0.05). The MP and NC-siRNA+MP groups had significantly higher mRNA and protein expression of AnxA2 than the AnxA2 siRNA+MP group (P<0.05). Compared with the control group, the MP and NC-siRNA+MP groups had significant increases in the protein expression of p-EGFR, p-p65 NF-κB, MUC5AC, and MUC5B (P<0.05); the AnxA2 siRNA+MP group had lower protein expression than the MP and NC-siRNA+MP groups, but higher protein expression than the control group (P<0.05).
Conclusions: AnxA2 is involved in the airway lesion induced by MP antigen via mediating EGFR/NF-κB signaling activation and mucin expression in human airway epithelial cells.
目的: 探讨沉默膜联蛋白A2(AnxA2)对肺炎支原体(MP)处理后人气道上皮细胞H292表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)/核因子κB(NF-κB)信号转导及黏蛋白表达的影响。
方法: 将H292细胞分为对照组、MP组、NC-siRNA+MP组和AnxA2 siRNA+MP组。MP组上皮细胞采用5 μg/mL MP抗原孵育2 h。NC-siRNA+MP组和AnxA2 siRNA+MP组细胞分别转染NC-siRNA和AnxA2 siRNA 24 h后用MP抗原刺激2 h。MTT法检测各组细胞活性;实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)检测各组细胞中AnxA2 mRNA的表达水平;Western blot法检测各组细胞AnxA2、磷酸化EGFR(p-EGFR)、磷酸化p65 NF-κB(p-p65 NF-κB)的表达水平;酶联免疫吸附试验检测黏蛋白5AC(MUC5AC)和黏蛋白5B(MUC5B)的分泌。
结果: MP组和NC-siRNA+MP组细胞活性低于对照组(P < 0.05),AnxA2 siRNA+MP组细胞活性高于MP组和NC-siRNA+MP组,但仍低于对照组(P < 0.05)。MP组和NC-siRNA+MP组AnxA2 mRNA和蛋白表达水平均明显高于AnxA2 siRNA+MP组(P < 0.05)。相比于对照组,MP组和NC-siRNA+MP组中p-EGFR、p-p65 NF-κB、MUC5AC和MUC5B的蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P < 0.05),AnxA2 siRNA+MP组上述蛋白表达水平则低于MP组和NC-siRNA+MP组,但仍高于对照组(P < 0.05)。
结论: AnxA2通过介导人气道上皮细胞EGFR/NF-κB信号活化和黏蛋白表达参与MP抗原诱导的气道病变。
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae modulates STAT3-STAT6/EGFR-FOXA2 signaling to induce overexpression of airway mucins.Infect Immun. 2014 Dec;82(12):5246-55. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01989-14. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 25287927 Free PMC article.
-
Resistin upregulates MUC5AC/B mucin gene expression in human airway epithelial cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 May 15;499(3):655-661. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.206. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29604272
-
Interleukin (IL) 36 gamma induces mucin 5AC, oligomeric mucus/gel-forming expression via IL-36 receptor-extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 and 2, and p38-nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells in human airway epithelial cells.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2018 Mar;32(2):87-93. doi: 10.1177/1945892418762844. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2018. PMID: 29644902
-
Annexin A2: A Double-Edged Sword in Pathogen Infection.Pathogens. 2024 Jul 4;13(7):564. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13070564. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39057791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Annexin A2: its molecular regulation and cellular expression in cancer development.Dis Markers. 2014;2014:308976. doi: 10.1155/2014/308976. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Dis Markers. 2014. PMID: 24591759 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous