Critical role of EphA4 in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rat
- PMID: 28698029
- PMCID: PMC6429031
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.07.003
Critical role of EphA4 in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rat
Abstract
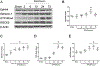
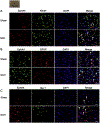
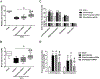
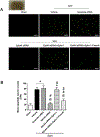
Early brain injury (EBI) is reported as a primary cause of mortality in subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) patients. Eph receptor A4 (EphA4) has been associated with blood-brain barrier integrity and pro-apoptosis. We aimed to investigate a role of EphA4 in EBI after SAH. One hundred and seventy-nine male adult Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into sham versus endovascular perforation model of SAH groups. SAH grade, neurological score, Evans blue dye extravasation, brain water content, mortality, Fluoro-Jade staining, immunofluorescence staining, and western blot experiments were performed after SAH. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) for EphA4, recombinant Ephexin-1 (rEphx-1), and Fasudil, a potent ROCK2 inhibitor, were used for intervention to study a role of EphA4 on EBI after SAH. The expression of EphA4, Ephexin-1, RhoA, and ROCK2 significantly increased after SAH. Knockdown of EphA4 using EphA4 siRNA injection intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v) reduced Evans blue extravasation, decreased brain water content, and alleviated neurobehavioral dysfunction after SAH. Additionally, the expression of Ephexin-1, RhoA, ROCK2 and cleaved caspase-3 were decreased. Tight junction proteins increased, and apoptotic neuron death decreased. The effects of EphA4 siRNA were abolished by rEphx-1. In contrast, Fasudil abolished the effects of rEphx-1. These results suggest that EphA4, a novel and promising target for treatment, exacerbates EBI through an Ephexin-1/ROCK2 pathway after SAH.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; EBI; EphA4; Neuronal apoptosis; Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures/conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Biervert HEC, Fahrig T, 2001. Semiquantitative expression analysis of ephrine-receptor tyrosine kinase mRNA’s in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Neurosci. Lett 315, 25–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

