APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B Activities Render Cancer Cells Susceptible to ATR Inhibition
- PMID: 28698210
- PMCID: PMC5609510
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-3389
APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B Activities Render Cancer Cells Susceptible to ATR Inhibition
Abstract
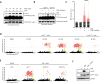
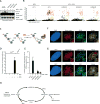
The apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme catalytic polypeptide-like APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B have emerged as key mutation drivers in cancer. Here, we show that APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B activities impose a unique type of replication stress by inducing abasic sites at replication forks. In contrast to cells under other types of replication stress, APOBEC3A-expressing cells were selectively sensitive to ATR inhibitors (ATRi), but not to a variety of DNA replication inhibitors and DNA-damaging drugs. In proliferating cells, APOBEC3A modestly elicited ATR but not ATM. ATR inhibition in APOBEC3A-expressing cells resulted in a surge of abasic sites at replication forks, revealing an ATR-mediated negative feedback loop during replication. The surge of abasic sites upon ATR inhibition associated with increased accumulation of single-stranded DNA, a substrate of APOBEC3A, triggering an APOBEC3A-driven feed-forward loop that ultimately drove cells into replication catastrophe. In a panel of cancer cell lines, ATRi selectively induced replication catastrophe in those harboring high APOBEC3A and/or APOBEC3B activities, showing that APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B activities conferred susceptibility to ATRi. Our results define an APOBEC-driven replication stress in cancer cells that may offer an opportunity for ATR-targeted therapy. Cancer Res; 77(17); 4567-78. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
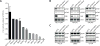
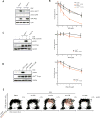
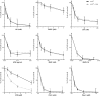
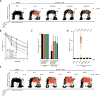
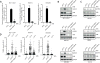
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Macheret M, Halazonetis TD. DNA replication stress as a hallmark of cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2015;10:425–448. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Horejsi Z, Koed K, Kramer A, Tort F, Zieger K, et al. DNA damage response as a candidate anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature. 2005;434:864–870. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M, Karakaidos P, Kletsas D, Issaeva N, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature. 2006;444:633–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

