GIGYF1/2 proteins use auxiliary sequences to selectively bind to 4EHP and repress target mRNA expression
- PMID: 28698298
- PMCID: PMC5538437
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.299420.117
GIGYF1/2 proteins use auxiliary sequences to selectively bind to 4EHP and repress target mRNA expression
Abstract
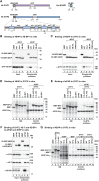
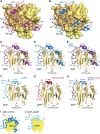
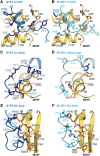
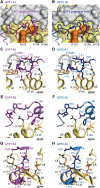
The eIF4E homologous protein (4EHP) is thought to repress translation by competing with eIF4E for binding to the 5' cap structure of specific mRNAs to which it is recruited through interactions with various proteins, including the GRB10-interacting GYF (glycine-tyrosine-phenylalanine domain) proteins 1 and 2 (GIGYF1/2). Despite its similarity to eIF4E, 4EHP does not interact with eIF4G and therefore fails to initiate translation. In contrast to eIF4G, GIGYF1/2 bind selectively to 4EHP but not eIF4E. Here, we present crystal structures of the 4EHP-binding regions of GIGYF1 and GIGYF2 in complex with 4EHP, which reveal the molecular basis for the selectivity of the GIGYF1/2 proteins for 4EHP. Complementation assays in a GIGYF1/2-null cell line using structure-based mutants indicate that 4EHP requires interactions with GIGYF1/2 to down-regulate target mRNA expression. Our studies provide structural insights into the assembly of 4EHP-GIGYF1/2 repressor complexes and reveal that rather than merely facilitating 4EHP recruitment to transcripts, GIGYF1/2 proteins are required for repressive activity.
Keywords: eIF4E; translational regulation; translational repression.
© 2017 Peter et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Repression of mRNA translation initiation by GIGYF1 via disrupting the eIF3-eIF4G1 interaction.Sci Adv. 2024 Jul 19;10(29):eadl5638. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adl5638. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39018414 Free PMC article.
-
4EHP-independent repression of endogenous mRNAs by the RNA-binding protein GIGYF2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jun 20;46(11):5792-5808. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky198. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29554310 Free PMC article.
-
Direct role for the Drosophila GIGYF protein in 4EHP-mediated mRNA repression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 26;47(13):7035-7048. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz429. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31114929 Free PMC article.
-
eIF4E-homologous protein (4EHP): a multifarious cap-binding protein.FEBS J. 2023 Jan;290(2):266-285. doi: 10.1111/febs.16275. Epub 2021 Nov 29. FEBS J. 2023. PMID: 34758096 Review.
-
GIGYF2: A Multifunctional Regulator at the Crossroads of Gene Expression, mRNA Surveillance, and Human Disease.Cells. 2025 Jul 5;14(13):1032. doi: 10.3390/cells14131032. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40643551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA-mediated translation repression through GYF-1 and IFE-4 in C. elegans development.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 May 21;49(9):4803-4815. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab162. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33758928 Free PMC article.
-
Low Expression of GIGYF1 Inhibits Metastasis, Proliferation, and Promotes Apoptosis and Autophagy of Gastric Cancer Cells.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Jun 12;20(8):1038-1045. doi: 10.7150/ijms.82719. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37484805 Free PMC article.
-
dCas13-mediated translational repression for accurate gene silencing in mammalian cells.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 11;15(1):2205. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46412-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38467613 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsically disordered regions of tristetraprolin and DCP2 directly interact to mediate decay of ARE-mRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Oct 14;50(18):10665-10679. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac797. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36130271 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for GIGYF-TNRC6 complex assembly.RNA. 2023 Jun;29(6):724-734. doi: 10.1261/rna.079596.123. Epub 2023 Feb 28. RNA. 2023. PMID: 36854607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cho PF, Poulin F, Cho-Park YA, Cho-Park IB, Chicoine JD, Lasko P, Sonenberg N. 2005. A new paradigm for translational control: inhibition via 5′–3′ mRNA tethering by Bicoid and the eIF4E cognate 4EHP. Cell 121: 411–423. - PubMed
-
- Gross JD, Moerke NJ, von der Haar T, Lugovskoy AA, Sachs AB, McCarthy JE, Wagner G. 2003. Ribosome loading onto the mRNA cap is driven by conformational coupling between eIF4G and eIF4E. Cell 115: 739–750. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
