Structure of the Arabidopsis TOPLESS corepressor provides insight into the evolution of transcriptional repression
- PMID: 28698367
- PMCID: PMC5544296
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1703054114
Structure of the Arabidopsis TOPLESS corepressor provides insight into the evolution of transcriptional repression
Abstract
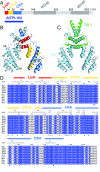
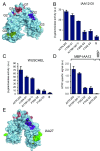
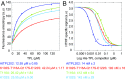
Transcriptional repression involves a class of proteins called corepressors that link transcription factors to chromatin remodeling complexes. In plants such as Arabidopsis thaliana, the most prominent corepressor is TOPLESS (TPL), which plays a key role in hormone signaling and development. Here we present the crystallographic structure of the Arabidopsis TPL N-terminal region comprising the LisH and CTLH (C-terminal to LisH) domains and a newly identified third region, which corresponds to a CRA domain. Comparing the structure of TPL with the mammalian TBL1, which shares a similar domain structure and performs a parallel corepressor function, revealed that the plant TPLs have evolved a new tetramerization interface and unique and highly conserved surface for interaction with repressors. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we validated those surfaces in vitro and in vivo and showed that TPL tetramerization and repressor binding are interdependent. Our results illustrate how evolution used a common set of protein domains to create a diversity of corepressors, achieving similar properties with different molecular solutions.
Keywords: TOPLESS; auxin signaling; corepressor; crystal structure; tetramerization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Perissi V, Jepsen K, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. Deconstructing repression: Evolving models of co-repressor action. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:109–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

