The Chemokine Receptor CXCR6 Evokes Reverse Signaling via the Transmembrane Chemokine CXCL16
- PMID: 28698473
- PMCID: PMC5535959
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18071468
The Chemokine Receptor CXCR6 Evokes Reverse Signaling via the Transmembrane Chemokine CXCL16
Abstract
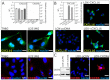
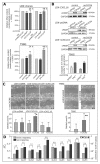
Reverse signaling is a signaling mechanism where transmembrane or membrane-bound ligands transduce signals and exert biological effects upon binding of their specific receptors, enabling a bidirectional signaling between ligand and receptor-expressing cells. In this study, we address the question of whether the transmembrane chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16, CXCL16 is able to transduce reverse signaling and investigate the biological consequences. For this, we used human glioblastoma cell lines and a melanoma cell line as in vitro models to show that stimulation with recombinant C-X-C chemokine receptor 6 (CXCR6) or CXCR6-containing membrane preparations induces intracellular (reverse) signaling. Specificity was verified by RNAi experiments and by transfection with expression vectors for the intact CXCL16 and an intracellularly-truncated form of CXCL16. We showed that reverse signaling via CXCL16 promotes migration in CXCL16-expressing melanoma and glioblastoma cells, but does not affect proliferation or protection from chemically-induced apoptosis. Additionally, fast migrating cells isolated from freshly surgically-resected gliomas show a differential expression pattern for CXCL16 in comparison to slowly-migrating cells, enabling a possible functional role of the reverse signaling of the CXCL16/CXCR6 pair in human brain tumor progression in vivo.
Keywords: brain tumor; cellular communication; chemokine; chemokine receptor; glioma; reverse signaling; tumor cell migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CXCL16/CXCR6 Axis Drives Microglia/Macrophages Phenotype in Physiological Conditions and Plays a Crucial Role in Glioma.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 27;9:2750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02750. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30542347 Free PMC article.
-
Irradiation of breast cancer cells enhances CXCL16 ligand expression and induces the migration of natural killer cells expressing the CXCR6 receptor.Cytotherapy. 2016 Dec;18(12):1532-1542. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.08.006. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Cytotherapy. 2016. PMID: 27720639
-
CXCL16/CXCR6 axis promotes bleomycin-induced fibrotic process in MRC-5 cells via the PI3K/AKT/FOXO3a pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Apr;81:106035. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106035. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31753588
-
The role of the CXCR6/CXCL16 axis in the pathogenesis of fibrotic disease.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 May 10;132:112015. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112015. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38608478 Review.
-
CXCR6/CXCL16 functions as a regulator in metastasis and progression of cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1806(1):42-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2010.01.004. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20122997 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of CXCL16 in the Pathogenesis of Cancer and Other Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 28;22(7):3490. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073490. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutaneous melanoma dissemination is dependent on the malignant cell properties and factors of intercellular crosstalk in the cancer microenvironment (Review).Int J Oncol. 2020 Sep;57(3):619-630. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5090. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Int J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32705148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Chemokine-Receptor Interactions and Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 14;18(11):2415. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112415. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29135930 Free PMC article.
-
Entry and exit of chemotherapeutically-promoted cellular dormancy in glioblastoma cells is differentially affected by the chemokines CXCL12, CXCL16, and CX3CL1.Oncogene. 2020 May;39(22):4421-4435. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1302-8. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32346064 Free PMC article.
-
A covalent creatine kinase inhibitor ablates glioblastoma migration and sensitizes tumors to oxidative stress.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 20;14(1):21959. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73051-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39304717 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

