The Application of REDOR NMR to Understand the Conformation of Epothilone B
- PMID: 28698492
- PMCID: PMC5535963
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18071472
The Application of REDOR NMR to Understand the Conformation of Epothilone B
Abstract
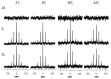
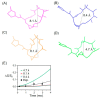
The structural information of small therapeutic compounds complexed in biological matrices is important for drug developments. However, structural studies on ligands bound to such a large and dynamic system as microtubules are still challenging. This article reports an application of the solid-state NMR technique to investigating the bioactive conformation of epothilone B, a microtubule stabilizing agent, whose analog ixabepilone was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as an anticancer drug. First, an analog of epothilone B was designed and successfully synthesized with deuterium and fluorine labels while keeping the high potency of the drug; Second, a lyophilization protocol was developed to enhance the low sensitivity of solid-state NMR; Third, molecular dynamics information of microtubule-bound epothilone B was revealed by high-resolution NMR spectra in comparison to the non-bound epothilone B; Last, information for the macrolide conformation of microtubule-bound epothilone B was obtained from rotational-echo double-resonance (REDOR) NMR data, suggesting the X-ray crystal structure of the ligand in the P450epoK complex as a possible candidate for the conformation. Our results are important as the first demonstration of using REDOR for studying epothilones.
Keywords: REDOR; bioactive conformation; epothilone B; microtubules; solid-state NMR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Crystal structures of epothilone D-bound, epothilone B-bound, and substrate-free forms of cytochrome P450epoK.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 7;278(45):44886-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308115200. Epub 2003 Aug 21. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12933799
-
Synthesis of isotopically labeled epothilones.J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2014 Feb;57(2):78-81. doi: 10.1002/jlcr.3144. Epub 2013 Dec 5. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2014. PMID: 24307484 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular recognition of epothilones by microtubules and tubulin dimers revealed by biochemical and NMR approaches.ACS Chem Biol. 2014 Apr 18;9(4):1033-43. doi: 10.1021/cb400673h. Epub 2014 Feb 25. ACS Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24524625
-
Epothilones as lead structures for the synthesis-based discovery of new chemotypes for microtubule stabilization.Acc Chem Res. 2008 Jan;41(1):21-31. doi: 10.1021/ar700157x. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Acc Chem Res. 2008. PMID: 18159935 Review.
-
Recent developments in the chemical biology of epothilones.Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(13):1595-613. doi: 10.2174/1381612053764715. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. PMID: 15892665 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

