Epigallocatechin Gallate Attenuates Hip Fracture-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Limiting Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Release
- PMID: 28698540
- PMCID: PMC5519220
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.902477
Epigallocatechin Gallate Attenuates Hip Fracture-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Limiting Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Release
Abstract
BACKGROUND To study the protective effects and explore the mechanism of epigallocatechingallate (EGCG) on the hip fracture-induced acute lung injury. MATERIAL AND METHODS Thirty male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into the control group, hip fracture group, and hip fracture + EGCG (10 mg/Kg) group. After 24 h, blood samples, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), and lung tissue were collected. Serum mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) was measured by RT-PCR and BALF was used to perform cytological analysis and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) assay. Lung tissue was used to evaluate the injury level. RESULTS EGCG significantly reduced the hip fracture-induced high level of serum mtDNA (p<0.05). HE staining showed protective effects of EGCG. Lower lung injury score and wet/dry ratio were identified in the hip fracture + EGCG group than in the hip fracture group (p<0.05). We found significantly lower levels of infiltration of inflammatory cells and production of inflammatory cytokines in the BALF of the hip fracture + EGCG group than in the hip fracture group (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS Our study found that EGCG had protective effects on hip fracture-induced acute lung injury and suggests that EGCG exerts its protective effects through limiting the release of mtDNA. Our results provide a novel pharmacological agent to attenuate hip fracture-induced acute lung injury, as well as a potential theory to better explain the anti-inflammatory property of EGCG.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


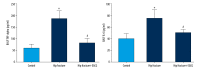
References
-
- Haleem S, Lutchman L, Mayahi R, et al. Mortality following hip fracture: Trends and geographical variations over the last 40 years. Injury. 2008;39:1157–63. - PubMed
-
- Sun T, Wang X, Liu Z, et al. Plasma concentrations of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and outcome prediction in elderly hip fracture patients. Injury. 2011;42:707–13. - PubMed
-
- Gan L, Chen X, Sun T, et al. The Significance of serum mtDNA concentration in lung injury induced by hip fracture. Shock. 2015;44(1):52–57. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

