SmMYB36, a Novel R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor, Enhances Tanshinone Accumulation and Decreases Phenolic Acid Content in Salvia miltiorrhiza Hairy Roots
- PMID: 28698552
- PMCID: PMC5506036
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-04909-w
SmMYB36, a Novel R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor, Enhances Tanshinone Accumulation and Decreases Phenolic Acid Content in Salvia miltiorrhiza Hairy Roots
Abstract
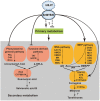
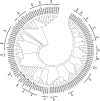
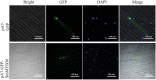
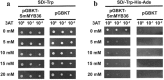
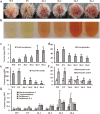
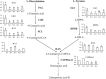
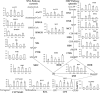
Phenolic acids and tanshinones are two major bioactive components in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. A novel endogenous R2R3-MYB transcription factor, SmMYB36, was identified in this research. This transcript factor can simultaneously influence the content of two types of components in SmMYB36 overexpression hairy roots. SmMYB36 was mainly localized in the nucleus of onion epidermis and it has transactivation activity. The overexpression of SmMYB36 promoted tanshinone accumulation but inhibited phenolic acid and flavonoid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. The altered metabolite content was due to changed metabolic flow which was regulated by transcript expression of metabolic pathway genes. The gene transcription levels of the phenylpropanoid general pathway, tyrosine derived pathway, methylerythritol phosphate pathway and downstream tanshinone biosynthetic pathway changed significantly due to the overexpression of SmMYB36. The wide distribution of MYB binding elements (MBS, MRE, MBSI and MBSII) and electrophoretic mobility shift assay results indicated that SmMYB36 may be an effective tool to regulate metabolic flux shifts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of SmbHLH148 induced biosynthesis of tanshinones as well as phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots.Plant Cell Rep. 2018 Dec;37(12):1681-1692. doi: 10.1007/s00299-018-2339-9. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Plant Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30229287
-
Overexpression of SmMYB9b enhances tanshinone concentration in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots.Plant Cell Rep. 2017 Aug;36(8):1297-1309. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2154-8. Epub 2017 May 15. Plant Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28508121
-
Metabolic engineering of artificially modified transcription factor SmMYB36-VP16 for high-level production of tanshinones and phenolic acids.Metab Eng. 2024 Nov;86:29-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2024.08.004. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Metab Eng. 2024. PMID: 39181435
-
The Biosynthetic Pathways of Tanshinones and Phenolic Acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza.Molecules. 2015 Sep 8;20(9):16235-54. doi: 10.3390/molecules200916235. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26370949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis and regulatory mechanism of tanshinones and phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza.Plant J. 2025 Jul;123(2):e70358. doi: 10.1111/tpj.70358. Plant J. 2025. PMID: 40720694 Review.
Cited by
-
The MYB transcription factor CiMYB42 regulates limonoids biosynthesis in citrus.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Jun 3;20(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02475-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32493275 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of two Pogostemon cablin chemotypes reveals genes related to patchouli alcohol biosynthesis.PeerJ. 2021 Aug 26;9:e12025. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12025. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34527441 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analyses revealed the ultraviolet B irradiation and phytohormone gibberellins coordinately promoted the accumulation of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L.Chin Med. 2020 Jul 1;15:67. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-00344-8. eCollection 2020. Chin Med. 2020. PMID: 32625243 Free PMC article.
-
Designing plant flavonoids: harnessing transcriptional regulation and enzyme variation to enhance yield and diversity.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jul 28;14:1220062. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1220062. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37575923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AtPAP1 Interacts With and Activates SmbHLH51, a Positive Regulator to Phenolic Acids Biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Nov 20;9:1687. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01687. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30515184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li LN. Biologically active components from traditional Chinese medicines: Pure and Applied Chemistry. Pure & Applied Chemistry. 1998;70:547–554.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

