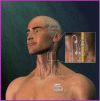
Vagus Nerve Stimulation
- PMID: 28698761
- PMCID: PMC5503741
- DOI: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.056
Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Abstract
Background: The vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is an approach mainly used in cases of intractable epilepsy despite all the efforts. Also, its benefits have been shown in severe cases of depression resistant to typical treatment.
Aim: The aim of this study was to present current knowledge of vagus nerve stimulation.
Material and methods: A new value has emerged just at this stage: VNS aiming the ideal treatment with new hopes. It is based on the placement of a programmable generator on the chest wall. Electric signals from the generator are transmitted to the left vagus nerve through the connection cable. Control on the cerebral bioelectrical activity can be achieved by way of these signal sent from there in an effort for controlling the epileptic discharges.
Results: The rate of satisfactory and permanent treatment in epilepsy with monotherapy is around 50%. This rate will increase by one-quarters (25%) with polytherapy. However, there is a patient group roughly constituting one-thirds of this population, and this group remains unresponsive or refractory to all the therapies and combined regimes. The more the number of drugs used, the more chaos and side effects are observed. The anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) used will have side effects on both the brain and the systemic organs. Cerebral resection surgery can be required in some patients. The most commonly encountered epilepsy type is the partial one, and the possibility of benefiting from invasive procedures is limited in most patients of this type. Selective amygdala-hippocampus surgery is a rising value in complex partial seizures. Therefore, as epilepsy surgery can be performed in very limited numbers and rather developed centres, success can also be achieved in limited numbers of patients. The common ground for all the surgical procedures is the target of preservation of memory, learning, speaking, temper and executive functions as well as obtaining a good control on seizures. However, the action mechanism of VNS is still not exactly known. On the other hand, it appears to be a reliable method that is tolerated well in partial resistant seizures. It has been observed that adverse effects are generally of mild-medium severity, and most of the problems can be eliminated easily through the re-adjustment of the stimulator.
Conclusion: VNS, which is a treatment modality that will take place it deserves in epilepsy treatment with "the correct patient" and "correct reason", must be known better and its applications must be developed.
Keywords: Vagus nerve stimulation; refractory seizure; treatment of epilepsy.
Similar articles
-
Vagus nerve stimulation therapy in partial epilepsy: a review.Acta Neurol Belg. 2016 Sep;116(3):241-8. doi: 10.1007/s13760-016-0616-3. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Acta Neurol Belg. 2016. PMID: 26908034 Review.
-
Vagus nerve stimulation for seizures.Arch Med Res. 2000 May-Jun;31(3):300-3. doi: 10.1016/s0188-4409(00)00060-6. Arch Med Res. 2000. PMID: 11036181 Review.
-
Vagus nerve stimulation: current status and clinical applications.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 1997 Oct;6(10):1327-35. doi: 10.1517/13543784.6.10.1327. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 1997. PMID: 15989504
-
Vagus nerve stimulation for intractable epilepsy: outcome in two series combining 90 patients.Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2007;97(Pt 2):287-91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-211-33081-4_32. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2007. PMID: 17691315 Clinical Trial.
-
Vagus nerve stimulation.Epilepsia. 1998 Jul;39(7):677-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1998.tb01151.x. Epilepsia. 1998. PMID: 9670894 Review.
Cited by
-
Vagus nerve stimulation in cerebral stroke: biological mechanisms, therapeutic modalities, clinical applications, and future directions.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Aug 1;19(8):1707-1717. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.389365. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38103236 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology to Risk Factor and Therapeutics to Treatment Strategies on Epilepsy.Brain Sci. 2024 Jan 10;14(1):71. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14010071. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38248286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of vagal activity may help reduce neurodevelopmental damage in the offspring of mothers with pre-eclampsia.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 2;14:1280334. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1280334. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022681 Free PMC article.
-
Bradyarrhythmia secondary to vagus nerve stimulator 7 years after placement.BMJ Case Rep. 2020 Jun 30;13(6):e235514. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-235514. BMJ Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32606132 Free PMC article.
-
MicroCT optimisation for imaging fascicular anatomy in peripheral nerves.J Neurosci Methods. 2020 May 15;338:108652. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108652. Epub 2020 Mar 13. J Neurosci Methods. 2020. PMID: 32179090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Groves DA, Brown VJ. Vagal nerve stimulation: a review of its applications and potential mechanisms that mediate its clinical effects. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 2005;29:493–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.01.004 . PMid:15820552. - PubMed
-
- Amar AP, Levy ML, Apuzzoc MLJ. In: Vagus nerve stimulation for intractable epilepsy, in Neurosurgical Operative Atlas. Rengechary S, editor. Vol. 9. Chicago, IL: American Association of Neurological Surgeons; 2000. pp. 179–188.
-
- Ben-Menachem E. Vagus nerve stimulation, side effects, and long-term safety. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2001;18(5):415–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004691-200109000-00005 . PMid:11709646. - PubMed
-
- Groves DA, Brown VJ. Vagal nerve stimulation: a review of its applications and potential mechanisms that mediate its clinical effects. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 2005;29:493–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.01.004 . PMid:15820552. - PubMed
-
- Penry JK, Dean JC. Prevention of intractable partial seizures by intermittent vagal stimulation in humans: preliminary results. Epilepsia. 1990;31(Suppl 2):40–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1990.tb05848.x . - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources