Proliferation of Interstitial Cells in the Cyclophosphamide-Induced Cystitis and the Preventive Effect of Imatinib
- PMID: 28698872
- PMCID: PMC5494099
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/3457093
Proliferation of Interstitial Cells in the Cyclophosphamide-Induced Cystitis and the Preventive Effect of Imatinib
Abstract
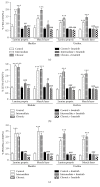
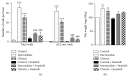
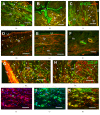
Cyclophosphamide- (CYP-) induced cystitis in the rat is a well-known model of bladder inflammation that leads to an overactive bladder, a process that appears to involve enhanced nitric oxide (NO) production. We investigated the changes in the number and distribution of interstitial cells (ICs) and in the expression of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) in the bladder and urethra of rats subjected to either intermediate or chronic CYP treatment. Pronounced hyperplasia and hypertrophy of ICs were evident within the lamina propria and in the muscle layer. IC immunolabeling with CD34, PDGFRα, and vimentin was enhanced, as reflected by higher colocalization indexes of the distinct pairs of markers. Moreover, de novo expression of eNOS was evident in vimentin and CD34 positive ICs. Pretreatment with the receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor Imatinib prevented eNOS expression and ICs proliferation, as well as the increased voiding frequency and urinary tract weight provoked by CYP. As similar results were obtained in the urethra, urethritis may contribute to the uropathology of CYP-induced cystitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Imatinib Mesylate Reduces Neurotrophic Factors and pERK and pAKT Expression in Urinary Bladder of Female Mice With Cyclophosphamide-Induced Cystitis.Front Syst Neurosci. 2022 Apr 22;16:884260. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2022.884260. eCollection 2022. Front Syst Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35528149 Free PMC article.
-
Altered neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression in the bladder and urethra of cyclophosphamide-treated rats.Nitric Oxide. 2014 May 30;39:8-19. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Nitric Oxide. 2014. PMID: 24731840
-
Imatinib Mesylate Reduces Voiding Frequency in Female Mice With Acute Cyclophosphamide-Induced Cystitis.Front Syst Neurosci. 2022 May 13;16:867875. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2022.867875. eCollection 2022. Front Syst Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35645740 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of transforming growth factor-β isoforms and cognate receptors in the rat urinary bladder following cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013 Nov 1;305(9):F1265-76. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00042.2013. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23926183 Free PMC article.
-
Neural upregulation in interstitial cystitis.Urology. 2007 Apr;69(4 Suppl):24-33. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2006.08.1108. Urology. 2007. PMID: 17462476 Review.
Cited by
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 4 (TRPV4) in urinary bladder structure and function.Curr Top Membr. 2022;89:95-138. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2022.06.002. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Curr Top Membr. 2022. PMID: 36210154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics as a Complementary Technique to Characterize Bladder Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 4;13(21):5537. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215537. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the molecular fingerprint of bladder and kidney fibroblasts.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 Dec 1;325(6):F826-F856. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00284.2023. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37823192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies of ultrastructure, gene expression, and marker analysis reveal that mouse bladder PDGFRA+ interstitial cells are fibroblasts.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022 Sep 1;323(3):F299-F321. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00135.2022. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35834272 Free PMC article.
-
Imatinib Mesylate Reduces Neurotrophic Factors and pERK and pAKT Expression in Urinary Bladder of Female Mice With Cyclophosphamide-Induced Cystitis.Front Syst Neurosci. 2022 Apr 22;16:884260. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2022.884260. eCollection 2022. Front Syst Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35528149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ribeiro R. A., Lima-Junior R. C. P., Leite C. A. V. G., et al. Chemotherapy-induced hemorrhagic cystitis: pathogenesis, pharmacological approaches and new insights. Journal of Experimental and Integrative Medicine. 2012;2(2):95–112.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

