Reversible Hypokalemia and Bartter-Like Syndrome during Prolonged Systemic Therapy with Colistimethate Sodium in an Adult Patient
- PMID: 28699114
- PMCID: PMC5505885
- DOI: 10.1007/s40800-017-0052-1
Reversible Hypokalemia and Bartter-Like Syndrome during Prolonged Systemic Therapy with Colistimethate Sodium in an Adult Patient
Abstract
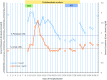
We present the case of a 58-year-old woman who developed hypokalaemia and metabolic alkalosis 2 weeks after therapy with colistimethate sodium for the treatment of chronic lower limb ulcer infection by extensively drug-resistant (XDR) Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The metabolic changes observed resembled Bartter syndrome, a group of congenital disorders affecting the distal segments of the renal tubules. The metabolic abnormalities reversed spontaneously 6 days after drug discontinuation. Acquired forms of Bartter syndrome have been reported during courses of antibiotic therapy; however, to our knowledge, this is the first documented case associated with colistimethate therapy in an adult.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
No funds were received in support of this work.
Conflict of interest
Tarek Kamal Eldin, Grazia Tosone, Alfredo Capuano and Raffaele Orlando have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics
The patient provided written informed consent for publication of this case report. A copy of the written consent may be requested for review from the corresponding author.
Figures
References
-
- Goodman L, Gilman A, Brunton L. Goodman and Gilman’s manual of pharmacology and therapeutics. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2011.
-
- Magiorakos A-P, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(3):268–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kellum J, Lameire N, Aspelin P, Barsoum RS, Burdmann E, Goldstein SL, et al. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2:1–138. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

