Salivary alpha-amylase, salivary cortisol, and anxiety during a youth taekwondo championship: An observational study
- PMID: 28700470
- PMCID: PMC5515742
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007272
Salivary alpha-amylase, salivary cortisol, and anxiety during a youth taekwondo championship: An observational study
Abstract
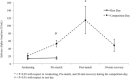
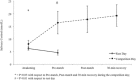
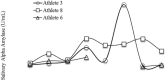
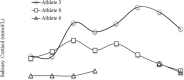
The aim of this study was to assess the stress-related responses and the coach's capability to match perceived efforts of youth athletes during a taekwondo championship.Using a cross-sectional study design, salivary cortisol (sC) and alpha-amylase (sAA) were measured in 6 males and 3 females young (11.0 ± 0.9 years) athletes at awakening, 5 minutes before, and 1 minute and 30 minutes after official combats. State anxiety was recorded 60 minutes before the first competition, whereas coach's and athletes' ratings of perceived exertion (RPE) were obtained at the end of the combats. Time-matched (awakening and pre-competition) salivary samples and trait anxiety were collected 7-day postcompetition during a resting day.No effect for match outcome emerged. No difference emerged between athletes and coach RPEs. Higher (P = .03) state anxiety (41.6 ± 10.9 points) was shown than trait anxiety (34.8 ± 7.1 points). Time-matched sAA were similar. Peak sAA observed at the end of the combat (114.2 ± 108.1 U/mL) was higher (P < .01) than the other samples (range: 20.6-48.1 U/mL), whereas sC increased (P < .05) from awakening (8.0 ± 1.5 nmol/L), with peak levels observed at 30 minutes into the recovery phase (19.3 ± 4.3 nmol/L). Furthermore, pre-competition sC (16.5 ± 4.5 nmol/L) values were higher (P < .01) with respect to time-matched samples during the resting day (4.6 ± 1.0 nmol/L). The 3 athletes engaged in consecutive matches showed a tendency toward increasing sAA and sC.Taekwondo combats pose a high stress on young athletes, eliciting a fast reactivity of the sympathetic-adreno-medullary system relative to the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical system. Understanding the athlete's efforts during combats, coaches are recommended to apply effective recovery strategies between matches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salivary cortisol and alpha-amylase reactivity to taekwondo competition in children.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012 Feb;112(2):647-52. doi: 10.1007/s00421-011-2023-z. Epub 2011 Jun 4. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21643917
-
Stress-related hormonal and psychological changes to official youth Taekwondo competitions.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2011 Feb;21(1):111-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2009.01046.x. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2011. PMID: 20030779
-
The Psychophysiologic Stress and Salivary Cortisol and Alpha-Amylase Awakening Responses to Cross-Country Running Competitions in National-Level Female Athletes.J Strength Cond Res. 2025 May 1;39(5):e676-e683. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000005055. Epub 2025 Mar 4. J Strength Cond Res. 2025. PMID: 40030101
-
Rating of Perceived Exertion for Quantification of Training and Combat Loads During Combat Sport-Specific Activities: A Short Review.J Strength Cond Res. 2017 Oct;31(10):2889-2902. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002047. J Strength Cond Res. 2017. PMID: 28933715 Review.
-
Physical and physiological profiles of taekwondo athletes.Sports Med. 2014 Jun;44(6):713-33. doi: 10.1007/s40279-014-0159-9. Sports Med. 2014. PMID: 24549477 Review.
Cited by
-
Anxiety and Emotional Intelligence: Comparisons Between Combat Sports, Gender and Levels Using the Trait Meta-Mood Scale and the Inventory of Situations and Anxiety Response.Front Psychol. 2020 Feb 4;11:130. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00130. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32116933 Free PMC article.
-
Competitive anxiety or Coronavirus anxiety? The psychophysiological responses of professional football players after returning to competition during the COVID-19 pandemic.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2021 Jul;129:105269. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2021.105269. Epub 2021 May 14. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2021. PMID: 34049198 Free PMC article.
-
Cananga odorata Aromatherapy Reduces Anxiety in Unexperienced Patients Hospitalized for Interventional Neuroradiology Procedures: A Randomized Control Trial.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2023 Jan-Dec;28:2515690X221150527. doi: 10.1177/2515690X221150527. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 36659818 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Relationship between Anxiety and Salivary Alpha-Amylase Levels in Mothers of Neonates Admitted to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.Iran J Child Neurol. 2023 Spring;17(2):55-61. doi: 10.22037/ijcn.v17i2.34910. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Iran J Child Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37091474 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Anterior-Posterior Spine Curvatures and Incidence of Sagittal Defects in Children and Adolescents Practicing Traditional Karate.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Apr 28;2019:9868473. doi: 10.1155/2019/9868473. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31183382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Federazione Italiana Taekwondo. 2013. Regolamento gara di combattimento. Available at: www.taekwondowtf.it. Accessed May 21, 2012.
-
- Chiodo S, Tessitore A, Cortis C, et al. Stress-related hormonal and psychological changes to official youth Taekwondo competitions. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2011;21:111–9. - PubMed
-
- Capranica L, Lupo C, Cortis C, et al. Salivary cortisol and alpha-amylase reactivity to taekwondo competition in children. Eur J Appl Physiol 2012;112:647–52. - PubMed
-
- Bridge CA, Jones MA, Drust B. Physiological responses and perceived exertion during international taekwondo competition. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 2009;4:485–93. - PubMed
-
- Chiodo S, Tessitore A, Cortis C, et al. Effects of official Taekwondo competitions on all-out performances of elite athletes. J Strength Cond Res 2011;25:334–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

