The prognostic and clinicopathologic characteristics of CD147 and esophagus cancer: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 28700599
- PMCID: PMC5507401
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180271
The prognostic and clinicopathologic characteristics of CD147 and esophagus cancer: A meta-analysis
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: The prognostic and clinicopathologic characteristics of CD147 and esophagus cancer: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 22;18(2):e0282229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282229. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36812187 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: The prognostic significance of CD147 expression in esophageal cancer patients remains controversial. Using a meta-analysis, we investigated the prognostic and clinicopathologic characteristics of CD147 in esophageal cancer.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search of the PubMed (1966-2016), EMBASE (1980-2016), Cochrane Library (1996-2016), Web of Science (1945-2016), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (1982-2016), and Wanfang databases (1988-2016) was performed to identify studies of all esophageal cancer subtypes. Correlations between CD147 expression and survival outcomes and clinicopathological features were analyzed using meta-analysis methods.
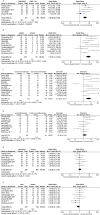
Results: Seventeen studies were included. High CD147 expression reduced the 3-year survival rate (OR = 3.26, 95% CI = (1.53, 6.93), p = 0.02) and 5-year survival rate(OR = 4.35, 95% CI = (2.13, 8.90), p < 0.0001). High CD147 expression reduced overall survival in esophageal cancer (HR = 1.60, 95% CI = (1.19, 2.15), p = 0.02). Additionally, higher CD147 expression was detected in esophageal cancer tissues than noncancerous tissues (OR = 9.45, 95% CI = (5.39, 16.59), p < 0.00001), normal tissues (OR = 12.73, 95% CI = (3.49, 46.46), p = 0.0001), para-carcinoma tissues (OR = 12.80, 95% CI = (6.57, 24.92), p < 0.00001), and hyperplastic tissues (OR = 3.27, 95% CI = (1.47, 7.29), p = 0.004). CD147 expression was associated with TNM stage (OR = 3.66, 95% CI = (2.20, 6.09), p < 0.00001), tumor depth (OR = 7.97, 95% CI = (4.13, 15.38), p < 0.00001), and lymph node status (OR = 5.14, 95% CI = (2.03,13.01), p = 0.0005), but not with tumor differentiation, age, or sex.
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis suggests that CD147 is an efficient prognostic factor in esophageal cancer. High CD147 expression in patients with esophageal cancer was associated with worse survival outcomes and common clinicopathological indicators of poor prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Siegel R, Ma JMandZou ZH. ct al. Cancer Statistics, 2014. Ca Cancer J Clin. 2014; 64(1–21.
-
- Tang WR, Fang JY, Wu KS, Shi XJ, Luo JYandLin K. Epidemiological characteristics and prediction of esophageal cancer mortality in China from 1991 to 2012. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014; 15(16):6929–34. - PubMed
-
- Jiang L, Zhao X, Meng XandYu J. Involved field irradiation for the treatment of esophageal cancer: is it better than elective nodal irradiation? CANCER LETT. 2015; 357(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.11.045 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Latif MM, Kelleher DandReynolds JV. Molecular mechanisms of constitutive and inducible NF-kappaB activation in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. EUR J CANCER. 2015; 51(4):464–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.11.014 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Ye SB, Ma G, Tang XF, Chen SP, He J, Liu WL, Xie D, Zeng YXandLi J. The expressions of MIF and CXCR4 protein in tumor microenvironment are adverse prognostic factors in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J TRANSL MED. 2013; 11(60 doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-60 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

