Gallic acid/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex: Improving solubility for application on in vitro/ in vivo Candida albicans biofilms
- PMID: 28700692
- PMCID: PMC5507443
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181199
Gallic acid/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex: Improving solubility for application on in vitro/ in vivo Candida albicans biofilms
Abstract
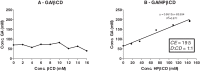
The aim of this study was to increase the solubility of gallic acid (GA) for the treatment of Candida albicans biofilm, which is very difficult to treat and requires high drug concentrations. Cyclodextrins (CDs) were used for this purpose. Complexes were evaluated by phase-solubility studies, prepared by spray drying and characterized by drug loading, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The complexes were tested on C. albicans biofilm using in vitro and in vivo models. HPβCD formed soluble inclusion complexes with GA. The percentage of GA in GA/HPβCD was 10.8 ± 0.01%. The SEM and DSC analyses confirmed the formation of inclusion complexes. GA/HPβCD maintained the antimicrobial activity of the pure GA. GA/HPβCD was effective on C. albicans biofilms of 24 and 48h. The in vivo results showed an anti-inflammatory activity of GA/HPβCD with no difference in invading hypha counting among the groups. This study encourages the development of new antifungal agents.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ. Epidemiology of invasive candidiasis: a persistent public health problem. Clinical microbiology reviews. 2007;20(1):133–63. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00029-06 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uppuluri P, Pierce CG, López-Ribot JL. Candida albicans biofilm formation and its clinical consequences. Future Microbiology. 2009;4(10):1235–7. doi: 10.2217/fmb.09.85 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Douglas LJ. Candida biofilms and their role in infection. Trends in Microbiology. 2003;11(1):30–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0966-842X(02)00002-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bujdáková H. Management of Candida biofilms: state of knowledge and new options for prevention and eradication. Future Microbiology. 2016;11(2):235–51. doi: 10.2217/fmb.15.139 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

