New Highly Sensitive Real-Time PCR Assay for HIV-2 Group A and Group B DNA Quantification
- PMID: 28701422
- PMCID: PMC5648720
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00755-17
New Highly Sensitive Real-Time PCR Assay for HIV-2 Group A and Group B DNA Quantification
Abstract
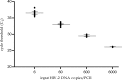
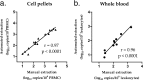
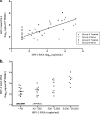
HIV-2 infection is characterized by a very low replication rate in most cases and low progression. This necessitates an approach to patient monitoring that differs from that for HIV-1 infection. Here, a new highly specific and sensitive method for HIV-2 DNA quantification was developed. The new test is based on quantitative real-time PCR targeting the long terminal repeat (LTR) and gag regions and using an internal control. Analytical performance was determined in three laboratories, and clinical performance was determined on blood samples from 63 patients infected with HIV-2 group A (n = 35) or group B (n = 28). The specificity was 100%. The 95% limit of detection was three copies/PCR and the limit of quantification was six copies/PCR. The within-run coefficients of variation were between 1.03% at 3.78 log10 copies/PCR and 27.02% at 0.78 log10 copies/PCR. The between-run coefficient of variation was 5.10%. Both manual and automated nucleic acid extraction methods were validated. HIV-2 DNA loads were detectable in blood cells from all 63 patients. When HIV-2 DNA was quantifiable, median loads were significantly higher in antiretroviral-treated than in naive patients and were similar for groups A and B. HIV-2 DNA load was correlated with HIV-2 RNA load (r = 0.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.4 to 0.8; P < 0.0001). Our data show that this new assay is highly sensitive and quantifies the two main HIV-2 groups, making it useful for the diagnosis of HIV-2 infection and for pathogenesis studies on HIV-2 reservoirs.
Keywords: DNA; HIV-2; PCR; quantification.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- De Cock KM, Brun-Vézinet F. 1989. Epidemiology of HIV-2 infection. AIDS 3 Suppl 1:S89–S95. - PubMed
-
- Matheron S, Pueyo S, Damond F, Simon F, Leprêtre A, Campa P, Salamon R, Chêne G, Brun-Vezinet F, French HIV-2 Cohort Study Group. 2003. Factors associated with clinical progression in HIV-2 infected-patients: the French ANRS cohort. AIDS 17:2593–2601. doi:10.1097/00002030-200312050-00006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burgard M, Jasseron C, Matheron S, Damond F, Hamrene K, Blanche S, Faye A, Rouzioux C, Warszawski J, Mandelbro L, ANRS French Perinatal Cohort EPF-CO1. 2010. Mother-to-child transmission of HIV-2 infection from 1986 to 2007 in the ANRS French Perinatal Cohort EPF-CO1. Clin Infect Dis 51:833–843. doi:10.1086/656284. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

