Chronic cholecystitis in the pediatric population: an underappreciated disease process
- PMID: 28702136
- PMCID: PMC5495900
Chronic cholecystitis in the pediatric population: an underappreciated disease process
Abstract
Aim: We hypothesize that chronic cholecystitis accounts for the majority of inflammatory diseases in the pediatric population and it is difficult to predict with preoperative ultrasound.
Background: Despite the increase in gallbladder disease, there is a paucity of data on pediatric cholecystitis. Most pediatric studies focus on cholelithiasis and biliary dyskinesia rather than inflammatory gallbladder disease.
Methods: We performed a single center retrospective review of all patients who underwent cholecystectomy from 1/1/10 - 1/1/15. Relevant data was extracted, including age, sex, acute vs. chronic presentation, duration of symptoms, preoperative imaging findings, and surgical pathology results.
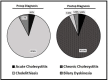
Results: Out of the 170 patients identified, there were 129 (75.9%) females and 41 (24.1%) males. The average age was 14 years (range 4-23 years). Seventy-six patients presented with acute symptoms with an average duration of pain of 2 days. Ninety-four patients presented with chronic symptoms and had an average duration of pain of 7.4 months. Eight patients (4.7%) had preoperative ultrasound that suggested inflammation, while the remaining showed only cholelithiasis. Pathology revealed chronic cholecystitis in 148 (87.1%). Among those who had pathologic evidence of chronic cholecystitis, preoperative inflammation was seen in only 5 patients (3.3%).
Conclusion: Chronic cholecystitis accounts for the majority of pediatric inflammatory diseases. These data suggest that most pediatric patients experience episodes of inflammation prior to cholecystectomy. Underappreciated gallbladder inflammation may delay surgical referral, increase emergency department and primary doctor visits, and lead to more difficult operations. Surgeons should consider early cholecystectomy when cholelithiasis and symptoms are present.
Keywords: Cholecystitis; Diagnosis; Intervention; Pediatric; Timing.
Figures
References
-
- Mehta S, Lopez ME, Chumpitazi BP, Mazziotti MV, Brandt ML, Fishman DS. Clinical characteristics and risk factors for symptomatic pediatric gallbladder disease. Pediatrics. 2012;129:e82–8. - PubMed
-
- Silva IV, Reis AF, Palaré MJ, Ferrão A, Rodrigues T, Morais A. Sickle cell disease in children: chronic complications and search of predictive factors for adverse outcomes. Eur J Haematol. 2015;94:157–61. - PubMed
-
- Srinath A, Saps M, Bielefeldt K. Biliary dyskinesia in pediatrics. Pediatr Ann. 2014;43:e83–8. - PubMed
-
- Soper NJ. Cholecystectomy: from Langenbuch to natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery. World J Surg. 2011;35:1422–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources