Fluorescent Probes with Multiple Binding Sites for the Discrimination of Cys, Hcy, and GSH
- PMID: 28703457
- PMCID: PMC6342557
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201704084
Fluorescent Probes with Multiple Binding Sites for the Discrimination of Cys, Hcy, and GSH
Abstract
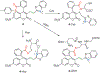
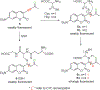
Biothiols such as cysteine (Cys), homocysteine (Hcy), and glutathione (GSH) play crucial roles in maintaining redox homeostasis in biological systems. This Minireview summarizes the most significant current challenges in the field of thiol-reactive probes for biomedical research and diagnostics, emphasizing the needs and opportunities that have been under-investigated by chemists in the selective probe and sensor field. Progress on multiple binding site probes to distinguish Cys, Hcy, and GSH is highlighted as a creative new direction in the field that can enable simultaneous, accurate ratiometric monitoring. New probe design strategies and researcher priorities can better help address current challenges, including the monitoring of disease states such as autism and chronic diseases involving oxidative stress that are characterized by divergent levels of GSH, Cys, and Hcy.
Keywords: biothiols; detection methods; fluorescence; imaging; multiple-binding-site probes.
© 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
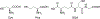

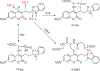
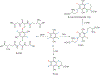
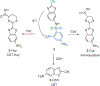
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

