Autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases: pathogenesis and therapy
- PMID: 28703923
- PMCID: PMC5739982
- DOI: 10.1111/bpa.12545
Autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases: pathogenesis and therapy
Abstract
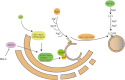
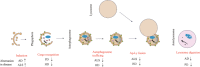
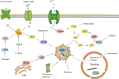
The most prevalent pathological features of many neurodegenerative diseases are the aggregation of misfolded proteins and the loss of certain neuronal populations. Autophagy, as major intracellular machinery for degrading aggregated proteins and damaged organelles, has been reported to be involved in the occurrence of pathological changes in many neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In this review, we summarize most recent research progress in this topic and provide a new perspective regarding autophagy regulation on the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Finally, we discuss the signaling molecules in autophagy-related pathways as therapeutic targets for the treatment of these diseases.
Keywords: autophagy; neurodegenerative diseases; protein aggregation.
© 2017 International Society of Neuropathology.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

