Effects of D1 and D2 receptor antagonists on the discriminative stimulus effects of methylendioxypyrovalerone and mephedrone in male Sprague-Dawley rats trained to discriminate D-amphetamine
- PMID: 28704276
- PMCID: PMC5599327
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000328
Effects of D1 and D2 receptor antagonists on the discriminative stimulus effects of methylendioxypyrovalerone and mephedrone in male Sprague-Dawley rats trained to discriminate D-amphetamine
Abstract
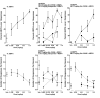
Psychopharmacology research has amassed substantial evidence for similarities between synthetic cathinones and other commonly abused psychostimulants. Few studies have utilized drug discrimination methods to investigate synthetic cathinones, and the precise neurochemical substrates underlying their interoceptive effects have not been examined. The present study assessed the involvement of D1 and D2 dopaminergic receptors in the stimulus effects of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) and mephedrone (MEPH) in rats trained to discriminate D-amphetamine. Eight male Sprague-Dawley rats were trained to discriminate 0.5 mg/kg D-amphetamine (AMPH) from saline. Dose-response curves were then generated with AMPH (0.0-1.0 mg/kg), MDPV (0.0-1.0 mg/kg), and MEPH (0.0-2.0 mg/kg). Subsequently, Sch 39166 (0.3 mg/kg) and haloperidol (0.5 mg/kg) were administered in combination with select doses of MDPV and MEPH. Both MDPV and MEPH produced full substitution for AMPH. Sch 39166 produced a downward shift in the MDPV and MEPH dose-response curves and haloperidol produced similar results with MDPV. These preliminary findings indicate that MDPV and MEPH produce interoceptive stimuli that are similar to those produced by AMPH and that D1 and D2 dopamine receptors contribute to these effects. Additional studies are warranted to investigate the contribution of other receptor mechanisms involved in the interoceptive stimuli produced by synthetic cathinones.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential effects of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) and 4-methylmethcathinone (mephedrone) in rats trained to discriminate MDMA or a d-amphetamine + MDMA mixture.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016 Feb;233(4):673-80. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4142-4. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016. PMID: 26558618 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of monoaminergic mechanisms to the discriminative stimulus effects of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in Sprague-Dawley rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Mar;236(3):963-971. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5145-8. Epub 2018 Dec 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30554256 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone discrimination in female Sprague-Dawley rats.Behav Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 1;32(6):524-532. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000647. Behav Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34397448 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral pharmacology of designer cathinones: a review of the preclinical literature.Life Sci. 2014 Feb 27;97(1):27-30. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.10.033. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24231450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotoxicology of Synthetic Cathinone Analogs.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2017;32:209-230. doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_21. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27753008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine-like discriminative stimulus effects of seven cathinones in rats.Behav Pharmacol. 2020 Jun;31(4):378-384. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000540. Behav Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31895060 Free PMC article.
-
Abuse potential and toxicity of the synthetic cathinones (i.e., "Bath salts").Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020 Mar;110:150-173. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.07.015. Epub 2019 May 14. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020. PMID: 31101438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of dopaminergic and serotonergic compounds in rats trained to discriminate a high and a low training dose of the synthetic cathinone mephedrone.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Mar;236(3):1015-1029. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05241-z. Epub 2019 Apr 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30980094 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular and Locomotor Effects of Binary Mixtures of Common "Bath Salts" Constituents: Studies with Methylone, MDPV, and Caffeine in Rats.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 2:2024.01.31.578069. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.31.578069. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Br J Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;182(8):1836-1855. doi: 10.1111/bph.17444. PMID: 38352520 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Cardiovascular and locomotor effects of binary mixtures of common 'bath salts' constituents: Studies with methylone, methylenedioxypyrovalerone and caffeine in rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;182(8):1836-1855. doi: 10.1111/bph.17444. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39843219
References
-
- Baumann MH, Partilla JS, Lehner KR, Thorndike EB, Hoffman AF, Holy M, et al. Powerful cocaine-like actions of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV), a principal constituent of psychoactive ‘bath salts’ products. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012;38(4):552–562. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.204. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Callahan PM, Appel JB, Cunningham KA. Dopamine D1 and D2 mediation of the discriminative stimulus properties of d-amphetamine and cocaine. Psychopharmacology. 1991;103(1):50–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

