Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) may play a major role in risk stratification based on cerebral oxygen saturation by near-infrared spectroscopy in patients undergoing major cardiovascular surgery
- PMID: 28704502
- PMCID: PMC5507540
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181154
Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) may play a major role in risk stratification based on cerebral oxygen saturation by near-infrared spectroscopy in patients undergoing major cardiovascular surgery
Abstract
Purpose: A previous study reported that low baseline cerebral oxygen saturation (ScO2) (≤50%) measured with near-infrared spectroscopy was predictive of poor clinical outcomes after cardiac surgery. However, such findings have not been reconfirmed by others. We conducted the current study to evaluate whether the previous findings would be reproducible, and to explore mechanisms underlying the ScO2-based outcome prediction.
Methods: We retrospectively investigated 573 consecutive patients, aged 20 to 91 (mean ± standard deviation, 67.1 ± 12.8) years, who underwent major cardiovascular surgery. Preanesthetic baseline ScO2, lowest intraoperative ScO2, various clinical variables, and hospital mortality were examined.
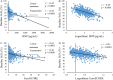
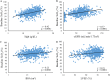
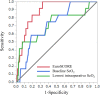
Results: Bivariate regression analyses revealed that baseline ScO2 correlated significantly with plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration (BNP), hemoglobin concentration (Hgb), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (p < 0.0001 for each). Baseline ScO2 correlated with BNP in an exponential manner, and BNP was the most significant factor influencing ScO2. Logistic regression analyses revealed that baseline and lowest intraoperative ScO2 values, but not relative ScO2 decrements, were significantly associated with hospital mortality (p < 0.05), independent of the EuroSCORE (p < 0.01). Receiver operating curve analysis of ScO2 values and hospital mortality revealed an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.715 (p < 0.01) and a cutoff value of ≤50.5% for the baseline and ScO2, and an AUC of 0.718 (p < 0.05) and a cutoff value of ≤35% for the lowest intraoperative ScO2. Low baseline ScO2 (≤50%) was associated with increases in intubation time, intensive care unit stay, hospital stay, and hospital mortality.
Conclusion: Baseline ScO2 was reflective of severity of systemic comorbidities and was predictive of clinical outcomes after major cardiovascular surgery. ScO2 correlated most significantly with BNP in an exponential manner, suggesting that BNP plays a major role in the ScO2-based outcome prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and Hemoglobin are Two Major Factors Significantly Associated With Baseline Cerebral Oxygen Saturation Measured Using the INVOS Oximeter in Patients Undergoing Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2018 Feb;32(1):187-196. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2017.04.018. Epub 2017 Apr 13. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2018. PMID: 28778770
-
Association of early perioperative stroke after cardiothoracic surgery with intraoperative regional cerebral oxygenation using near-infrared spectroscopy: an observational cohort study comparing affected versus non-affected hemispheres.J Clin Monit Comput. 2025 Apr;39(2):271-281. doi: 10.1007/s10877-024-01241-3. Epub 2024 Nov 20. J Clin Monit Comput. 2025. PMID: 39565465
-
Preoperative cerebral oxygen saturation and clinical outcomes in cardiac surgery.Anesthesiology. 2011 Jan;114(1):58-69. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181fef34e. Anesthesiology. 2011. PMID: 21178669
-
Prognostic value of brain natriuretic peptide in noncardiac surgery: a meta-analysis.Anesthesiology. 2009 Aug;111(2):311-9. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181aaeb11. Anesthesiology. 2009. PMID: 19602961 Review.
-
Clinical Applications of Near-infrared Spectroscopy Monitoring in Cardiovascular Surgery.Anesthesiology. 2021 May 1;134(5):784-791. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000003700. Anesthesiology. 2021. PMID: 33529323 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regional cerebral oxygen saturation during initial mobilization of critically ill patients is associated with clinical outcomes: a prospective observational study.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2025 Feb 3;13(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40635-025-00722-2. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2025. PMID: 39899079 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma brain natriuretic peptide is a biomarker for screening ischemic cerebral small vessel disease in patients with hypertension.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(35):e12088. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012088. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30170428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng F, Sheinberg R, Yee MS, Ono M, Zheng Y, Hogue CW. Cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy monitoring and neurologic outcomes in adult cardiac surgery patients: a systematic review. Anesth analg. 2013;116: 663–76. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e318277a255 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Steppan J, Hogue CW Jr. Cerebral and tissue oximetry. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2014;28: 429–39. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2014.09.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yao FS, Tseng CC, Ho CY, Levin SK, Illner P. Cerebral oxygen desaturation is associated with early postoperative neuropsychological dysfunction in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2004;18: 552–8. - PubMed
-
- Reents W, Muellges W, Franke D, Babin-Ebell J, Elert O. Cerebral oxygen saturation assessed by near-infrared spectroscopy during coronary artery bypass grafting and early postoperative cognitive function. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;74: 109–14. - PubMed
-
- Hong SW, Shim JK, Choi YS, Kim DH, Chang BC, Kwak YL. Prediction of cognitive dysfunction and patients' outcome following valvular heart surgery and the role of cerebral oximetry. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;33: 560–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2008.01.012 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

