Serotype-specific role of antigen I/II in the initial steps of the pathogenesis of the infection caused by Streptococcus suis
- PMID: 28705175
- PMCID: PMC5513104
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-017-0443-4
Serotype-specific role of antigen I/II in the initial steps of the pathogenesis of the infection caused by Streptococcus suis
Abstract
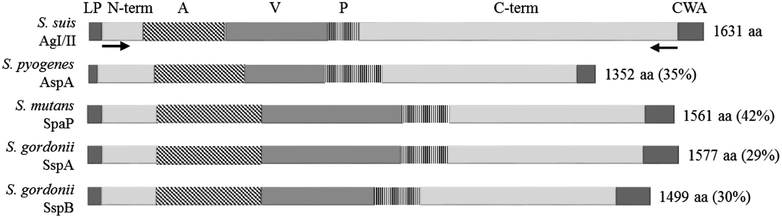
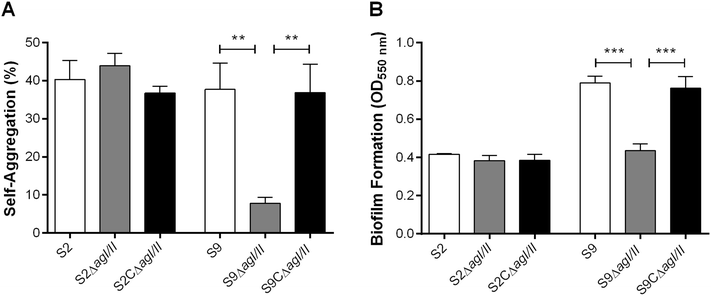
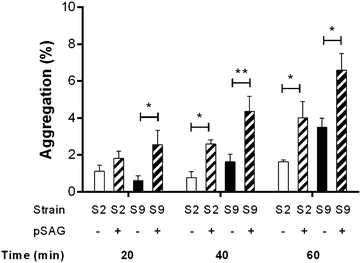
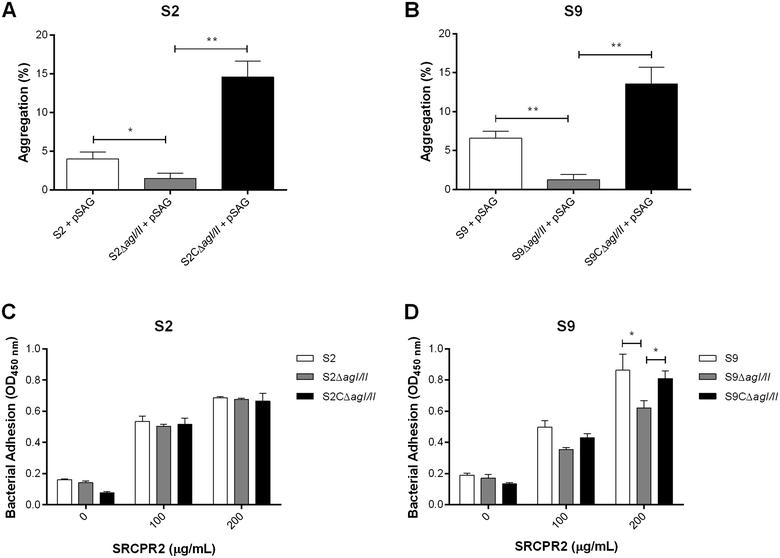
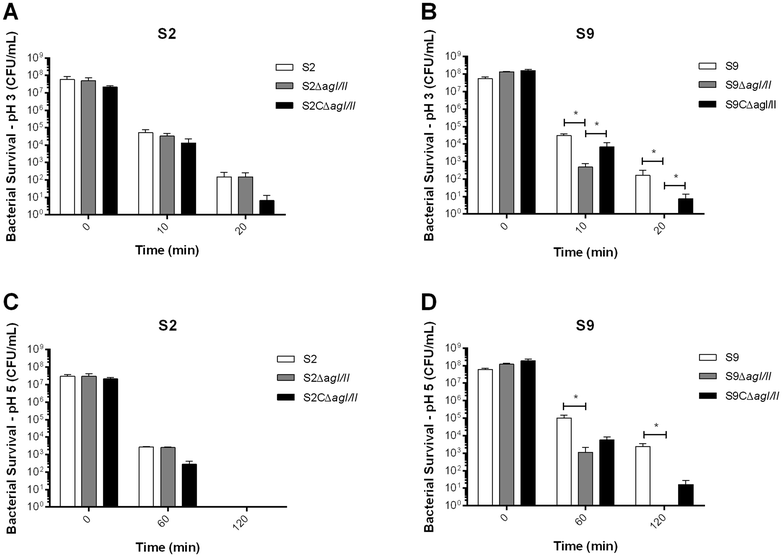
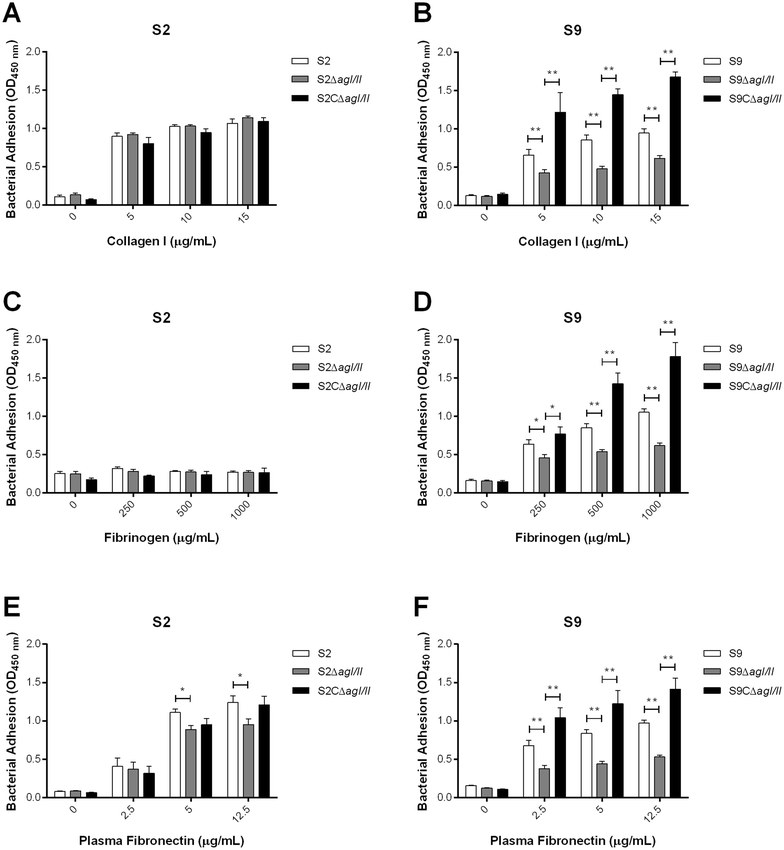
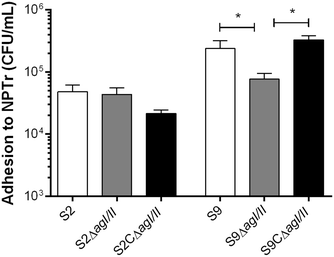
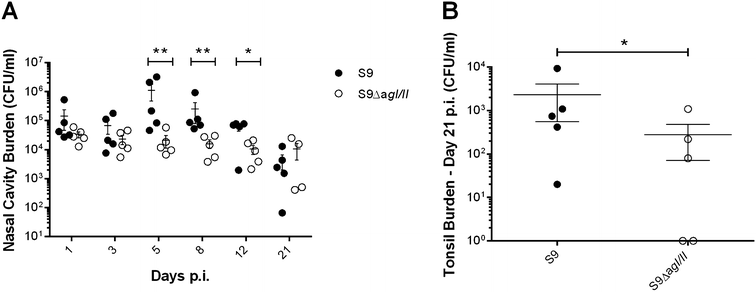
Streptococcus suis is one of the most important post-weaning porcine bacterial pathogens worldwide. The serotypes 2 and 9 are often considered the most virulent and prevalent serotypes involved in swine infections, especially in Europe. However, knowledge of the bacterial factors involved in the first steps of the pathogenesis of the infection remains scarce. In several pathogenic streptococci, expression of multimodal adhesion proteins known as antigen I/II (AgI/II) have been linked with persistence in the upper respiratory tract and the oral cavity, as well as with bacterial dissemination. Herein, we report expression of these immunostimulatory factors by S. suis serotype 2 and 9 strains and that AgI/II-encoding genes are carried by integrative and conjugative elements. Using mutagenesis and different in vitro assays, we demonstrate that the contribution of AgI/II to the virulence of the serotype 2 strain used herein appears to be modest. In contrast, data demonstrate that the serotype 9 AgI/II participates in self-aggregation, induces salivary glycoprotein 340-related aggregation, contributes to biofilm formation and increased strain resistance to low pH, as well as in bacterial adhesion to extracellular matrix proteins and epithelial cells. Moreover, the use of a porcine infection model revealed that AgI/II contributes to colonization of the upper respiratory tract of pigs. Taken together, these findings suggest that surface exposed AgI/II likely play a key role in the first steps of the pathogenesis of the S. suis serotype 9 infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antigen I/II Participates in the Interactions of Streptococcus suis Serotype 9 With Phagocytes and the Development of Systemic Disease.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 24;9:124. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00124. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31069179 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Streptococcus suis isolates from the diseased pigs in China between 2003 and 2007.Vet Microbiol. 2009 May 28;137(1-2):196-201. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.12.015. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Vet Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19185432
-
The protective protein Sao (surface antigen one) is not a critical virulence factor for Streptococcus suis serotype 2.Microb Pathog. 2014 Feb-Mar;67-68:31-5. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2014.02.002. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Microb Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24530923
-
Surface-associated and secreted factors of Streptococcus suis in epidemiology, pathogenesis and vaccine development.Anim Health Res Rev. 2009 Jun;10(1):65-83. doi: 10.1017/S146625230999003X. Anim Health Res Rev. 2009. PMID: 19558750 Review.
-
The pathogenesis of the meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis: the unresolved questions.Vet Microbiol. 2000 Oct 1;76(3):259-72. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(00)00250-9. Vet Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10973700 Review.
Cited by
-
The Integrative Conjugative Element clc (ICEclc) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa JB2.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jul 11;9:1532. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01532. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30050515 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin M-degrading enzyme of Streptococcus suis (Ide Ssuis ) impairs porcine B cell signaling.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 16;14:1122808. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1122808. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36875121 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcal autolysin promotes dysfunction of swine tracheal epithelium by interacting with vimentin.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Aug 3;18(8):e1010765. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010765. eCollection 2022 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35921364 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Nature of Streptococcal Antigen I/II Proteins in Colonization and Disease Pathogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2020 Nov 25;11:602305. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.602305. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33329493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipoteichoic acids influence cell shape and bacterial division of Streptococcus suis serotype 2, but play a limited role in the pathogenesis of the infection.Vet Res. 2024 Mar 19;55(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01287-w. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38504299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ye C, Zhu X, Jing H, Du H, Segura M, Zheng H, Kan B, Wang L, Bai X, Zhou Y, Cui Z, Zhang S, Jin D, Sun N, Luo X, Zhang J, Gong Z, Wang X, Wang L, Sun H, Li Z, Sun Q, Liu H, Dong B, Ke C, Yuan H, Wang H, Tian K, Wang Y, Gottschalk M, Xu J. Streptococcus suis sequence type 7 outbreak, Sichuan, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1203–1208. doi: 10.3201/eid1708.060232. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

