Detecting impaired myocardial relaxation in sepsis with a novel tissue Doppler parameter (septal e'/s')
- PMID: 28705247
- PMCID: PMC5512826
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1727-9
Detecting impaired myocardial relaxation in sepsis with a novel tissue Doppler parameter (septal e'/s')
Abstract
Background: Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction is associated with mortality outcomes in severe sepsis and septic shock. There are ongoing issues with diagnosing diastolic dysfunction in this cohort, partly owing to the poor applicability of traditional parameters in the hyperdynamic circulation. In this feasibility study, we sought to assess the utility of a novel parameter (septal e'/s') to identify diastolic dysfunction in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock who had normal systolic function against the 2016 American Society Echocardiography and European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (ASE/EACI) guidelines on diastolic dysfunction.
Methods: In this prospective observational pilot study, patients identified as having severe sepsis and septic shock underwent transthoracic echocardiography on day 1 and day 3 of their intensive care unit admission. In patients with normal systolic function, septal e'/s' was calculated using the peak modal velocity of the s' compared with the e' from the septal annulus tissue Doppler imaging and compared with their diastolic grade according to the 2016 ASE/EACI guidelines on diastolic dysfunction.
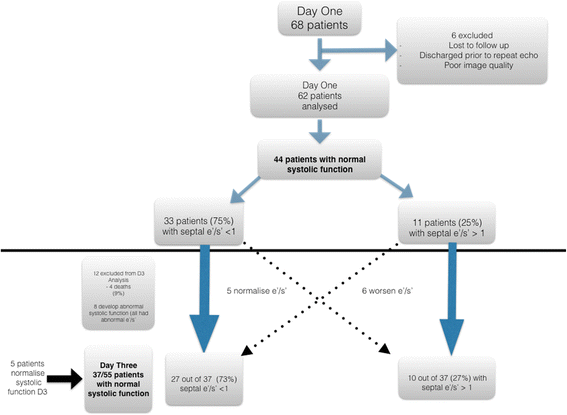
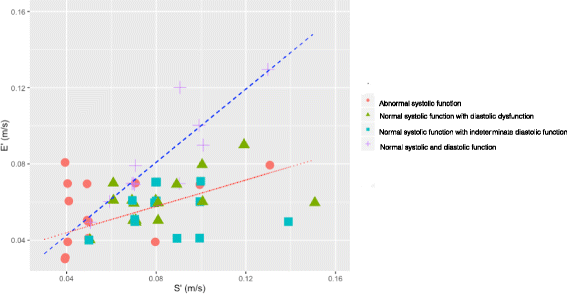
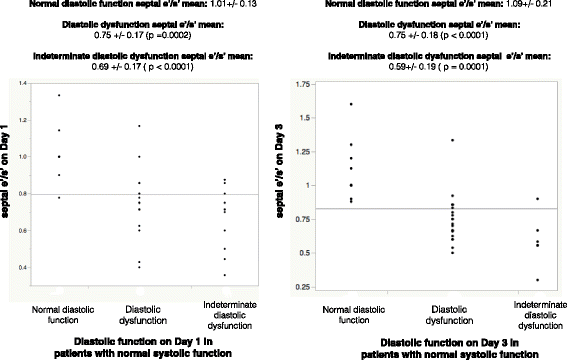
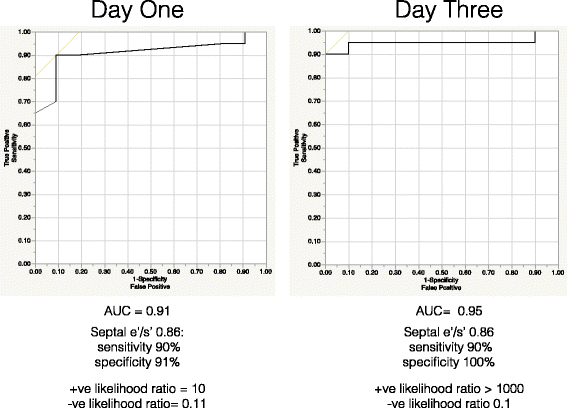
Results: On day 1 of admission, 44 of 62 patients with severe sepsis and septic shock had normal systolic function. There was a strong association of those with diastolic dysfunction having a reduced septal e'/s' compared with patients with normal diastolic function (AUC 0.91). A similar relationship was seen with patients who had indeterminate diastolic dysfunction. On day 3, 37 patients had normal systolic function. Again, there was a strong association of those with diastolic dysfunction and a reduced septal e'/s' (AUC 0.95).
Conclusions: A reduction in septal e'/s' may indicate diastolic dysfunction in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock who have normal systolic function. As opposed to limited traditional measures of diastolic dysfunction, it is applicable in those with hyperdynamic systolic function.
Keywords: Diastolic function; Myocardial relaxation; Sepsis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

