Efficient Generation of Dopamine Neurons by Synthetic Transcription Factor mRNAs
- PMID: 28705346
- PMCID: PMC5589083
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.06.015
Efficient Generation of Dopamine Neurons by Synthetic Transcription Factor mRNAs
Abstract
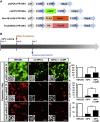
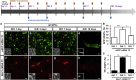
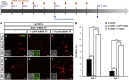
Generation of functional dopamine (DA) neurons is an essential step for the development of effective cell therapy for Parkinson's disease (PD). The generation of DA neurons can be accomplished by overexpression of DA-inducible genes using virus- or DNA-based gene delivery methods. However, these gene delivery methods often cause chromosomal anomalies. In contrast, mRNA-based gene delivery avoids this problem and therefore is considered safe to use in the development of cell-based therapy. Thus, we used mRNA-based gene delivery method to generate safe DA neurons. In this study, we generated transformation-free DA neurons by transfection of mRNA encoding DA-inducible genes Nurr1 and FoxA2. The delivery of mRNA encoding dopaminergic fate inducing genes proved sufficient to induce naive rat forebrain precursor cells to differentiate into neurons exhibiting the biochemical, electrophysiological, and functional properties of DA neurons in vitro. Additionally, the generation efficiency of DA neurons was improved by the addition of small molecules, db-cAMP, and the adjustment of transfection timing. The successful generation of DA neurons using an mRNA-based method offers the possibility of developing clinical-grade cell sources for neuronal cell replacement treatment for PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; dopamine neuron; genomic integration free; in vitro transcription; mRNA; neural precursor cell.
Copyright © 2017 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Foxa2 and Nurr1 synergistically yield A9 nigral dopamine neurons exhibiting improved differentiation, function, and cell survival.Stem Cells. 2010 Mar 31;28(3):501-12. doi: 10.1002/stem.294. Stem Cells. 2010. PMID: 20049900
-
Reprogramming astrocytes into dopaminergic neurons to restore motor dysfunction in Parkinson's disease model rats.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Sept 28;49(9):1377-1389. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240078. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39931768 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
In vitro generation of mature midbrain-type dopamine neurons by adjusting exogenous Nurr1 and Foxa2 expressions to their physiologic patterns.Exp Mol Med. 2017 Mar 10;49(3):e300. doi: 10.1038/emm.2016.163. Exp Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28280264 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Therapy for Parkinson's Disease Using Midbrain Developmental Genes to Regulate Dopaminergic Neuronal Maintenance.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 18;25(22):12369. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212369. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering a dopaminergic phenotype in stem/precursor cells: role of Nurr1, glia-derived signals, and Wnts.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 May;1049:51-66. doi: 10.1196/annals.1334.007. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 15965107 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced Cytotoxicity by Repetitive mRNA Transfection in Differentiated Neurons.Int J Stem Cells. 2023 Feb 28;16(1):117-122. doi: 10.15283/ijsc22125. Epub 2022 Dec 31. Int J Stem Cells. 2023. PMID: 36581368 Free PMC article.
-
Combining NGN2 programming and dopaminergic patterning for a rapid and efficient generation of hiPSC-derived midbrain neurons.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 13;12(1):17176. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22158-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36229560 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Assembly, Production, and Transfection of Synthetic Modified mRNA.Methods. 2018 Jan 15;133:29-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Methods. 2018. PMID: 29080741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park C.H., Minn Y.K., Lee J.Y., Choi D.H., Chang M.Y., Shim J.W., Ko J.Y., Koh H.C., Kang M.J., Kang J.S. In vitro and in vivo analyses of human embryonic stem cell-derived dopamine neurons. J. Neurochem. 2005;92:1265–1276. - PubMed
-
- Ko J.Y., Park C.H., Koh H.C., Cho Y.H., Kyhm J.H., Kim Y.S., Lee I., Lee Y.S., Lee S.H. Human embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors as a continuous, stable, and on-demand source for human dopamine neurons. J. Neurochem. 2007;103:1417–1429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

