Efficacy and safety of taxane-based systemic chemotherapy of advanced gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28706257
- PMCID: PMC5509659
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-05464-0
Efficacy and safety of taxane-based systemic chemotherapy of advanced gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Taxanes are chemotherapeutic agents commonly used to treat several cancers. However, the effects of taxanes on advanced gastric cancer (AGC) are still not clear, especially when used as a first-line treatment. This systematic review and meta-analysis aims to investigate the efficacy and safety of taxanes as a first-line treatment of AGC. The quality of our included studies was assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias tool for RCTs and NOS scale for nRCTs, and the data of the included studies was of satisfactory quality to analyze. The outcomes included overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), overall response rate (ORR), and toxicity. Taxanes significantly improved OS (HR = 0.84, 95% CI 0.76-0.92, P = 0.0004) and had a slight effect on ORR (RR = 1.23, 95% CI 1.00-1.51, P = 0.05). However, taxanes may also increase the risks of neutropenia and leucopenia, similar to effects observed in other conventional chemotherapeutic treatments such as oxaliplatin and epirubicin. Therefore, patient characteristics including concomitant diseases, physical condition, and prior therapies should be considered before selecting taxane-based treatments for AGC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

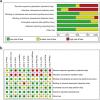


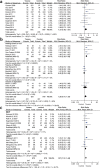
References
-
- Ochenduszko S, et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of first-line palliative chemotherapy with EOX and mDCF regimens in patients with locally advanced inoperable or metastatic HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: a randomized phase 3 trial. Med Oncol. 2015;32:242. doi: 10.1007/s12032-015-0687-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

