A Simple Add-and-Display Method for Immobilisation of Cancer Drug on His-tagged Virus-like Nanoparticles for Controlled Drug Delivery
- PMID: 28706267
- PMCID: PMC5509718
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-05525-4
A Simple Add-and-Display Method for Immobilisation of Cancer Drug on His-tagged Virus-like Nanoparticles for Controlled Drug Delivery
Abstract
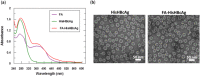
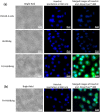
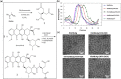
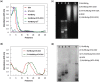
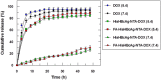
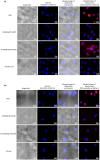
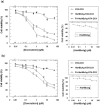
pH-responsive virus-like nanoparticles (VLNPs) hold promising potential as drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. In the present study, hepatitis B virus (HBV) VLNPs harbouring His-tags were used to display doxorubicin (DOX) via nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) conjugation. The His-tags served as pH-responsive nanojoints which released DOX from VLNPs in a controlled manner. The His-tagged VLNPs conjugated non-covalently with NTA-DOX, and cross-linked with folic acid (FA) were able to specifically target and deliver the DOX into ovarian cancer cells via folate receptor (FR)-mediated endocytosis. The cytotoxicity and cellular uptake results revealed that the His-tagged VLNPs significantly increased the accumulation of DOX in the ovarian cancer cells and enhanced the uptake of DOX, which improved anti-tumour effects. This study demonstrated that NTA-DOX can be easily displayed on His-tagged VLNPs by a simple Add-and-Display step with high coupling efficiency and the drug was only released at low pH in a controlled manner. This approach facilitates specific attachment of any drug molecule on His-tagged VLNPs at the very mild conditions without changing the biological structure and native conformation of the VLNPs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Shielding of Hepatitis B Virus-Like Nanoparticle with Poly(2-Ethyl-2-Oxazoline).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 3;20(19):4903. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194903. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31623310 Free PMC article.
-
A Dual Bioconjugated Virus-Like Nanoparticle as a Drug Delivery System and Comparison with a pH-Responsive Delivery System.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018 Apr 13;8(4):236. doi: 10.3390/nano8040236. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29652827 Free PMC article.
-
pH-responsive Virus-like Nanoparticles with Enhanced Tumour-targeting Ligands for Cancer Drug Delivery.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 24;6:37891. doi: 10.1038/srep37891. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27883070 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel folic acid receptor-targeted, β-cyclodextrin-based drug complexes for cancer treatment.PLoS One. 2013 May 2;8(5):e62289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062289. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658721 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer activity of released doxorubicin from a folate-mediated polyelectrolyte complex.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2011;22(11):1487-507. doi: 10.1163/092050610X512414. Epub 2010 Jul 12. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2011. PMID: 20626956
Cited by
-
Thermally-responsive Virus-like Particle for Targeted Delivery of Cancer Drug.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 8;9(1):3945. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40388-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30850643 Free PMC article.
-
Shielding of Hepatitis B Virus-Like Nanoparticle with Poly(2-Ethyl-2-Oxazoline).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 3;20(19):4903. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194903. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31623310 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-like nanoparticles as a theranostic platform for cancer.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jan 12;10:1106767. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1106767. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36714624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B Virus-Like Particle: Targeted Delivery of Plasmid Expressing Short Hairpin RNA for Silencing the Bcl-2 Gene in Cervical Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 26;22(5):2320. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052320. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33652577 Free PMC article.
-
A Dual Bioconjugated Virus-Like Nanoparticle as a Drug Delivery System and Comparison with a pH-Responsive Delivery System.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018 Apr 13;8(4):236. doi: 10.3390/nano8040236. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29652827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Y, Wang W, Yang J, Zhou C, Sun J. pH-sensitive polymeric micelles triggered drug release for extracellular and intracellular drug targeting delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013;8:159–167. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2013.07.021. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

