Qiliqiangxin Enhances Cardiac Glucose Metabolism and Improves Diastolic Function in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
- PMID: 28706558
- PMCID: PMC5494577
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/3197320
Qiliqiangxin Enhances Cardiac Glucose Metabolism and Improves Diastolic Function in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
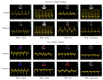
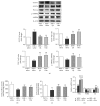
Cardiac diastolic dysfunction has emerged as a growing type of heart failure. The present study aims to explore whether Qiliqiangxin (QL) can benefit cardiac diastolic function in spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) through enhancement of cardiac glucose metabolism. Fifteen 12-month-old male SHRs were randomly divided into QL-treated, olmesartan-treated, and saline-treated groups. Age-matched WKY rats served as normal controls. Echocardiography and histological analysis were performed. Myocardial glucose uptake was determined by 18F-FDG using small-animal PET imaging. Expressions of several crucial proteins and key enzymes related to glucose metabolism were also evaluated. As a result, QL improved cardiac diastolic function in SHRs, as evidenced by increased E'/A'and decreased E/E' (P < 0.01). Meanwhile, QL alleviated myocardial hypertrophy, collagen deposits, and apoptosis (P < 0.01). An even higher myocardial glucose uptake was illustrated in QL-treated SHR group (P < 0.01). Moreover, an increased CS activity and ATP production was observed in QL-treated SHRs (P < 0.05). QL enhanced cardiac glucose utilization and oxidative phosphorylation in SHRs by upregulating AMPK/PGC-1α axis, promoting GLUT-4 expression, and regulating key enzymes related to glucose aerobic oxidation such as HK2, PDK4, and CS (P < 0.01). Our data suggests that QL improves cardiac diastolic function in SHRs, which may be associated with enhancement of myocardial glucose metabolism.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Qiliqiangxin Improves Cardiac Function through Regulating Energy Metabolism via HIF-1α-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms in Heart Failure Rats after Acute Myocardial Infarction.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jun 12;2020:1276195. doi: 10.1155/2020/1276195. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32626732 Free PMC article.
-
Olmesartan attenuates cardiac hypertrophy and improves cardiac diastolic function in spontaneously hypertensive rats through inhibition of calcineurin pathway.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014 Mar;63(3):218-26. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000038. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24603116
-
Qiliqiangxin improves cardiac function and attenuates cardiac remodeling in rats with experimental myocardial infarction.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):6596-606. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261541 Free PMC article.
-
Can 18F-FDG-PET show differences in myocardial metabolism between Wistar Kyoto rats and spontaneously hypertensive rats?Lab Anim. 2013 Oct;47(4):320-3. doi: 10.1177/0023677213495668. Epub 2013 Jul 14. Lab Anim. 2013. PMID: 23851029
-
Traditional Chinese Medication Qiliqiangxin Protects Against Cardiac Remodeling and Dysfunction in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats.Int J Med Sci. 2017 Apr 9;14(5):506-514. doi: 10.7150/ijms.18142. eCollection 2017. Int J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28539827 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Qiliqiangxin Capsules Optimize Cardiac Metabolism Flexibility in Rats With Heart Failure After Myocardial Infarction.Front Physiol. 2020 Jul 17;11:805. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00805. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32848816 Free PMC article.
-
Qili Qiangxin Capsule Combined With Sacubitril/Valsartan for HFrEF: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 4;13:832782. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.832782. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35444529 Free PMC article.
-
Searching for Effective Treatments in HFpEF: Implications for Modeling the Disease in Rodents.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;16(10):1449. doi: 10.3390/ph16101449. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Hypertension Affects Heart Metabolism.Front Physiol. 2019 Apr 16;10:435. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00435. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31040794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Nε-(carboxymethyl) lysine affects cardiac glucose metabolism and myocardial remodeling in mice.World J Diabetes. 2022 Nov 15;13(11):972-985. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.972. World J Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 36437860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mori J., Basu R., McLean B. A., et al. Agonist-induced hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction are associated with selective reduction in glucose oxidation: a metabolic contribution to heart failure with normal ejection fraction. Circulation Heart Failure. 2012;5(4):493–503. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.112.966705. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

