Rationale of Using Dynamic Imaging for Characterization of Suspicious Lung Masses into Benign or Malignant on Contrast Enhanced Multi Detector Computed Tomography
- PMID: 28706752
- PMCID: PMC5499391
- DOI: 10.4103/jcis.JCIS_18_17
Rationale of Using Dynamic Imaging for Characterization of Suspicious Lung Masses into Benign or Malignant on Contrast Enhanced Multi Detector Computed Tomography
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the utility of dynamic imaging namely, wash-in and wash-out characteristics through multidetector contrast-enhanced computed tomography in differentiating benign and malignant pulmonary masses.
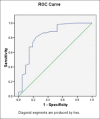
Materials and methods: Seventy-three patients who were suspected to have malignant pulmonary mass on the basis of clinical symptoms and chest radiograph were included in the study. All the patients underwent multidetector computed tomography scanning, and three series of images were obtained for each patient-noncontrast, early enhanced, and 15 min delayed enhanced scans. Computed tomography (CT) findings were assessed in terms of washin, absolute, and relative percentage washout of contrast. Biopsy of the mass was done and sent for histopathological evaluation. Sensitivity, specificity, and area under curve for diagnosing malignancy in the lung masses were calculated by considering both the wash-in and wash-out characteristics at dynamic CT and plotting the receiver operating curve after the final diagnosis which was obtained by histopathological evaluation.
Results: Threshold net enhancement (washin) value of >22.5 HU had sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy of 88.5%, 57.1%, and 82%, respectively, in predicting malignancy. Threshold relative percentage washout of <16.235% had 98.1%, 85.7%, and 94% sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy, respectively, and threshold absolute percentage washout of <42.72% had 98.1%, 95.2%, and 95% sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy, respectively, in predicting malignancy.
Conclusion: Threshold net enhancement (washin), absolute and relative washout percentages can be used to predict malignancy with very high diagnostic yield, and possibly obviate the need of invasive procedures for diagnosis of bronchogenic carcinoma.
Keywords: Contrast wash-in; contrast wash-out; histopathology; lung mass; multidetector computed tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Erasmus JJ, Connolly JE, McAdams HP, Roggli VL. Solitary pulmonary nodules: Part I. Morphologic evaluation for differentiation of benign and malignant lesions. Radiographics. 2000;20:43–58. - PubMed
-
- Swensen SJ, Viggiano RW, Midthun DE, Müller NL, Sherrick A, Yamashita K, et al. Lung nodule enhancement at CT: Multicenter study. Radiology. 2000;214:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Swensen SJ, Brown LR, Colby TV, Weaver AL, Midthun DE. Lung nodule enhancement at CT: Prospective findings. Radiology. 1996;201:447–55. - PubMed
-
- Yi CA, Lee KS, Kim EA, Han J, Kim H, Kwon OJ, et al. Solitary pulmonary nodules: Dynamic enhanced multi-detector row CT study and comparison with vascular endothelial growth factor and microvessel density. Radiology. 2004;233:191–9. - PubMed
-
- Swensen SJ, Brown LR, Colby TV, Weaver AL. Pulmonary nodules: CT evaluation of enhancement with iodinated contrast material. Radiology. 1995;194:393–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

