A computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) scheme for pretreatment prediction of pathological response to neoadjuvant therapy using dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI texture features
- PMID: 28707546
- PMCID: PMC5858803
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20170269
A computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) scheme for pretreatment prediction of pathological response to neoadjuvant therapy using dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI texture features
Abstract
Objective: To assess whether a computer-aided, diagnosis (CAD) system can predict pathological Complete Response (pCR) to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) prior to treatment using texture features.
Methods: Response to treatment of 44 patients was defined according to the histopatology of resected tumour and extracted axillary nodes in two ways: (a) pCR+ (Smith's Grade = 5) vs pCR- (Smith's Grade < 5); (b) pCRN+ (pCR+ and absence of residual lymph node metastases) vs pCRN - . A CAD system was developed to: (i) segment the breasts; (ii) register the DCE-MRI sequence; (iii) detect the lesion and (iv) extract 27 3D texture features. The role of individual texture features, multiparametric models and Bayesian classifiers in predicting patients' response to NAC were evaluated.
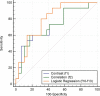
Results: A cross-validated Bayesian classifier fed with 6 features was able to predict pCR with a specificity of 72% and a sensitivity of 67%. Conversely, 2 features were used by the Bayesian classifier to predict pCRN, obtaining a sensitivity of 69% and a specificity of 61%.
Conclusion: A CAD scheme, that extracts texture features from an automatically segmented 3D mask of the tumour, could predict pathological response to NAC. Additional research should be performed to validate these promising results on a larger cohort of patients and using different classification strategies. Advances in knowledge: This is the first study assessing the role of an automatic CAD system in predicting the pathological response to NAC before treatment. Fully automatic methods represent the backbone of standardized analysis and may help in timely managing patients candidate to NAC.
Figures


References
-
- M Kaufmann, G von Minckwitz, R Smith, V Valero, L Gianni, W Eiermann, et al. International expert panel on the use of primary (preoperative) systemic treatment of operable breast cancer: review and recommendations. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 2600–8. - PubMed
-
- SD Heys, AW Hutcheon, TK Sarkar, KN Ogston, ID Miller, S Payne, et al. Neoadjuvant docetaxel in breast cancer: 3-year survival results from the aberdeen trial. Clin Breast Cancer 2002; 3(Suppl. 2): S69–S74. - PubMed
-
- B Fisher, J Bryant, N Wolmark, E Mamounas, A Brown, ER Fisher, et al. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on the outcome of women with operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 1919; 16: 2672–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

