Regulation of PLK1 through competition between hnRNPK, miR-149-3p and miR-193b-5p
- PMID: 28708135
- PMCID: PMC5635212
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2017.106
Regulation of PLK1 through competition between hnRNPK, miR-149-3p and miR-193b-5p
Abstract
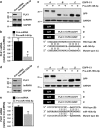
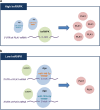
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a critical regulator of cell cycle progression and apoptosis. However, its regulation remains poorly understood. In the present study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the post-transcriptional regulation of PLK1. We observed that heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNPK) and PLK1 were positively associated in several different cancers and high expression levels of them correlated with poor prognosis in patients with cancer. Knockdown of hnRNPK resulted in reduced expression of PLK1, whereas conversely, PLK1 expression was increased in hnRNPK-overexpressing cells. We found that hnRNPK regulated PLK1 expression through KH1- and KH2-dependent interactions with the 3'UTR of PLK1 mRNA. In addition, microRNA-149-3p (miR-149-3p) and miR-193b-5p suppressed PLK1 expression by targeting the 3'UTR of PLK1 mRNA. MicroRNA-elicited enrichment of PLK1 mRNA in Ago2 immunoprecipitation was altered by the presence or absence of hnRNPK. Furthermore, the deletion of the cytosine (C)-rich sequences of the 3'UTR of PLK1 mRNA abolished the decreased PLK1 expression observed via hnRNPK silencing and administration of miRNAs, a finding that suggests that hnRNPK shares this C-rich motif with miR-149-3p and miR-193b-5p. We also found that downregulation of PLK1 by either silencing hnRNPK or overexpression of miR-149-3p and miR-193b-5p decreased clonogenicity and induced apoptosis. Our findings from this study demonstrate that hnRNPK regulates PLK1 expression by competing with the PLK1-targeting miRNAs, miR-149-3p and miR-193b-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
miR-296-5p suppresses cell viability by directly targeting PLK1 in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Rep. 2016 Jan;35(1):497-503. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4392. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26549165
-
MiR-296-5p suppresses papillary thyroid carcinoma cell growth via targeting PLK1.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Mar;23(5):2084-2091. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201903_17251. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30915753
-
MicroRNA-100 is a potential molecular marker of non-small cell lung cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting polo-like kinase 1.BMC Cancer. 2012 Nov 14;12:519. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-519. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23151088 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
The Mitotic Cancer Target Polo-Like Kinase 1: Oncogene or Tumor Suppressor?Genes (Basel). 2019 Mar 11;10(3):208. doi: 10.3390/genes10030208. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30862113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
hnRNPK-regulated LINC00263 promotes malignant phenotypes through miR-147a/CAPN2.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Mar 17;12(4):290. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03575-1. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33731671 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia-related kinase 2 drives pancreatic cancer progression by protecting Plk1 from Chfr-mediated degradation.Oncogene. 2021 Jul;40(28):4663-4674. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01893-4. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34140642
-
Pan-Cancer Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies PLK1 Crucial for the Tumorigenesis of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Feb 16;15:1099-1116. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S347732. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35210814 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00162 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by sponging PAQR4-targeting miR-485-5p.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Jul;237(7):2943-2960. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30758. Epub 2022 May 2. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35491694 Free PMC article.
-
AGO-RBP crosstalk on target mRNAs: Implications in miRNA-guided gene silencing and cancer.Transl Oncol. 2022 Jul;21:101434. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101434. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35477066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hamanaka R, Maloid S, Smith MR, O'Connell CD, Longo DL, Ferris DK. Cloning and characterization of human and murine homologues of the Drosophila polo serine-threonine kinase. Cell growth differ 1994; 5: 249–257. - PubMed
-
- Takai N, Hamanaka R, Yoshimatsu J, Miyakawa I. Polo-like kinases (Plks) and cancer. Oncogene 2005; 24: 287–291. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

