Quick or quality? How mRNA escapes nuclear quality control during stress
- PMID: 28708448
- PMCID: PMC5731798
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1345835
Quick or quality? How mRNA escapes nuclear quality control during stress
Abstract
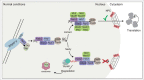
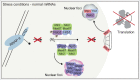
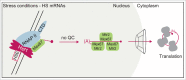
Understanding the mechanisms for mRNA production under normal conditions and in response to cytotoxic stresses has been subject of numerous studies for several decades. The shutdown of canonical mRNA transcription, export and translation is required to have enough free resources for the immediate production of heat shock proteins that act as chaperones to sustain cellular processes. In recent work we uncovered a simple mechanism, in which the export block of regular mRNAs and a fast export of heat shock mRNAs is achieved by deactivation of the nuclear mRNA quality control mediated by the guard proteins. In this point of view we combine long known data with recently gathered information that support this novel model, in which cells omit quality control of stress responsive transcripts to ensure survival.
Keywords: Heat stress; cellular stress; mRNA quality control; nuclear export.
Figures
References
-
- Meinel DM, Sträßer K. Co-transcriptional mRNP formation is coordinated within a molecular mRNP packaging station in S. cerevisiae. Bioessays 2015; 37:666-77; PMID:25801414; https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201400220 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Niño CA, Hérissant L, Babour A, Dargemont C. mRNA nuclear export in yeast. Chem Rev 2013; 113:8523-45; PMID:23731471; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400002g - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tutucci E, Stutz F. Keeping mRNPs in check during assembly and nuclear export. Nat Rev 2011; 12:377-84; PMID:21602906; https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3119 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hsin J-p, Manley JL. The RNA polymerase II CTD coordinates transcription and RNA processing. Genes Dev 2012; 26:2119-37; PMID:23028141; https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.200303.112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bataille AR, Jeronimo C, Jacques PÉ, Laramée L, Fortin MÈ, Forest A, Bergeron M, Hanes SD, Robert F. A universal RNA polymerase II CTD cycle is orchestrated by complex interplays between kinase, phosphatase, and isomerase enzymes along genes. Mol Cell 2012; 45:158-70; PMID:22284676; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.024 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
