HIV Viral Load Suppression in Adults and Children Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy-Results From the IeDEA Collaboration
- PMID: 28708808
- PMCID: PMC5634924
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001499
HIV Viral Load Suppression in Adults and Children Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy-Results From the IeDEA Collaboration
Abstract
Background: Having 90% of patients on antiretroviral therapy (ART) and achieving an undetectable viral load (VL) is 1 of the 90:90:90 by 2020 targets. In this global analysis, we investigated the proportions of adult and paediatric patients with VL suppression in the first 3 years after ART initiation.
Methods: Patients from the IeDEA cohorts who initiated ART between 2010 and 2014 were included. Proportions with VL suppression (<1000 copies/mL) were estimated using (1) strict intention to treat (ITT)-loss to follow-up (LTFU) and dead patients counted as having detectable VL; and (2) modified ITT-LTFU and dead patients were excluded. Logistic regression was used to identify predictors of viral suppression at 1 year after ART initiation using modified ITT.
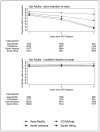
Results: A total of 35,561 adults from 38 sites/16 countries and 2601 children from 18 sites/6 countries were included. When comparing strict with modified ITT methods, the proportion achieving VL suppression at 3 years from ART initiation changed from 45.1% to 90.2% in adults, and 60.6% to 80.4% in children. In adults, older age, higher CD4 count pre-ART, and homosexual/bisexual HIV exposure were associated with VL suppression. In children, older age and higher CD4 percentage pre-ART showed significant associations with VL suppression.
Conclusions: Large increases in the proportion of VL suppression in adults were observed when we excluded those who were LTFU or had died. The increases were less pronounced in children. Greater emphasis should be made to minimize LTFU and maximize patient retention in HIV-infected patients of all age groups.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS. 90-90-90 An ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. [Accessed 30 September, 2015];2014 http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/90-90-90_en_0.pdf.
-
- World Health Organization. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treatment and preventing HIV infection: Recommendations for a public health approach. [Accessed January 8, 2014];2013 Jun; http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/85321/1/9789241505727_eng.pdf. - PubMed
-
- IeDEA. The International Epidemiologic Databases to Evaluate AIDS network. [Accessed 30 October, 2015];2015 http://www.iedea.org/
-
- Duda SN, Farr AM, Lindegren ML, et al. Characteristics and comprehensiveness of adult HIV care and treatment programmes in Asia-Pacific, sub-Saharan Africa and the Americas: results of a site assessment conducted by the International epidemiologic Databases to Evaluate AIDS (IeDEA) Collaboration. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19045. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Z01 CP010176/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069923/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI037613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA020790/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA016893/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI037984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103397/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA011602/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 EY013707/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA165937/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007583/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA000432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA036935/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007587/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA004334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI067039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008057/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008052/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI110527/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI093197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI065298/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069907/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103401/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA013566/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP055504/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002317/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000083/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000421/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103390/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103408/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA037788/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008067/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069924/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AA020794/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

