Trends of influenza B during the 2010-2016 seasons in 2 regions of north and south Italy: The impact of the vaccine mismatch on influenza immunisation strategy
- PMID: 28708953
- PMCID: PMC5861802
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1342907
Trends of influenza B during the 2010-2016 seasons in 2 regions of north and south Italy: The impact of the vaccine mismatch on influenza immunisation strategy
Abstract
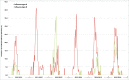
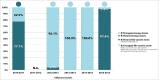
Influenza A and B viruses are responsible for respiratory infections, representing globally seasonal threats to human health. The 2 viral types often co-circulate and influenza B plays an important role in the spread of infection. A 6-year retrospective surveillance study was conducted between 2010 and 2016 in 2 large administrative regions of Italy, located in the north (Liguria) and in the south (Sicily) of the country, to describe the burden and epidemiology of both B/Victoria and B/Yamagata lineages in different healthcare settings. Influenza B viruses were detected in 5 of 6 seasonal outbreaks, exceeding influenza A during the season 2012-2013. Most of influenza B infections were found in children aged ≤ 14 y and significant differences were observed in the age-groups infected by the different lineages. B/Victoria strains prevailed in younger population than B/Yamagata, but also were more frequently found in the community setting. Conversely, B/Yamagata viruses were prevalent among hospitalized cases suggesting their potential role in the development of more severe disease. The relative proportions of viral lineages varied from year to year, resulting in different lineage-level mismatch for the B component of trivalent influenza vaccine. Our findings confirmed the need for continuous virological surveillance of seasonal epidemics and bring attention to the adoption of universal influenza immunization program in the childhood. The use of tetravalent vaccine formulations may be useful to improve the prevention and control of the influenza burden in general population.
Keywords: B/Victoria; B/Yamagata; Influenza type B; community; hospital; lineage; vaccine-mismatch.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-circulation of the two influenza B lineages during 13 consecutive influenza surveillance seasons in Italy, 2004-2017.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Nov 21;19(1):990. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4621-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31752738 Free PMC article.
-
Ten influenza seasons in France: distribution and timing of influenza A and B circulation, 2003-2013.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Aug 21;15:357. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1056-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26289794 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiology of influenza B virus and implications in immunization strategy, Southern Brazil.Vaccine. 2018 Jan 2;36(1):107-113. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.11.033. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 29174679
-
A comprehensive review of the epidemiology and disease burden of Influenza B in 9 European countries.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016 Apr 2;12(4):993-1002. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1111494. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016. PMID: 26890005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the case for trivalent or quadrivalent influenza vaccines.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016 Oct 2;12(10):2712-2717. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1091130. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016. PMID: 27435025 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Surveillance Data for Eight Consecutive Influenza Seasons in Sicily, Italy.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019 Dec;101(6):1232-1239. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0059. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019. PMID: 31571567 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine Mismatches, Viral Circulation, and Clinical Severity Patterns of Influenza B Victoria and Yamagata Infections in Brazil over the Decade 2010-2020: A Statistical and Phylogeny-Trait Analyses.Viruses. 2022 Jul 5;14(7):1477. doi: 10.3390/v14071477. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35891457 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and Genetic Variability of Circulating Influenza B Viruses in Uruguay, 2012-2019.Microorganisms. 2020 Apr 19;8(4):591. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8040591. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32325860 Free PMC article.
-
[Health Technology Assessment (HTA) of the introduction of influenza vaccination for Italian children with Fluenz Tetra®].J Prev Med Hyg. 2021 Sep 10;62(2 Suppl 1):E1-E118. doi: 10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.2s1. eCollection 2021 Jun. J Prev Med Hyg. 2021. PMID: 34909481 Free PMC article. Italian. No abstract available.
-
Epidemiology of Respiratory Pathogens among Elderly Nursing Home Residents with Acute Respiratory Infections in Corsica, France, 2013-2017.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:1423718. doi: 10.1155/2017/1423718. Epub 2017 Dec 17. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29392127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khieu TQ, Pierse N, Telfar-Barnard LF, Huang QS, Baker MG. Estimating the contribution of influenza to hospitalisations in New Zealand from 1994 to 2008. Vaccine 2015; 33(33):4087-92 pii: S0264-410X(15)00895-6; PMID:26143611; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.06.080 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Savy V, Ciapponi A, Bardach A, Glujovsky D, Aruj P, Mazzoni A, Gibbons L, Ortega-Barría E, Colindres RE. Burden of influenza in Latin America and the Caribbean: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 2013; 7(6):1017-32; PMID:23210504; doi: 10.1111/irv.12036 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
