The Enhanced Photo-Electrochemical Detection of Uric Acid on Au Nanoparticles Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode
- PMID: 28709376
- PMCID: PMC5509567
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-017-2225-3
The Enhanced Photo-Electrochemical Detection of Uric Acid on Au Nanoparticles Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode
Abstract
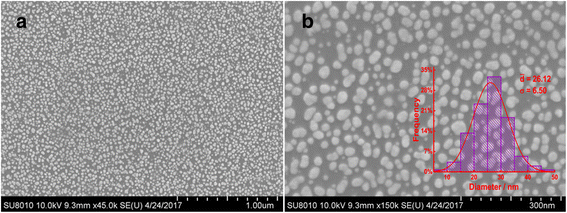
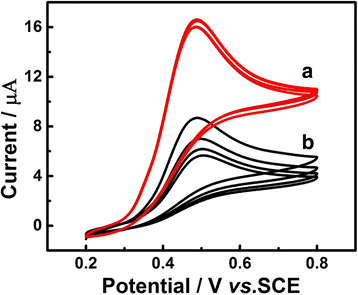
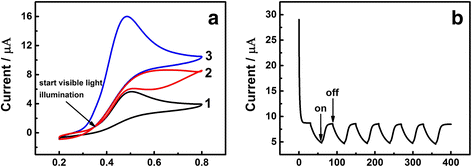
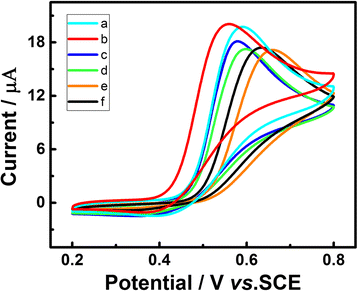
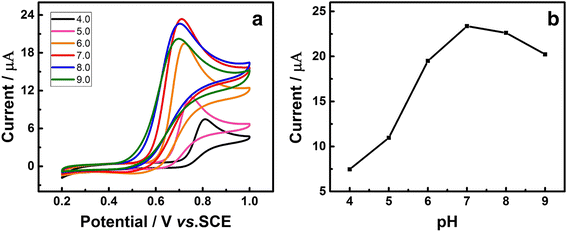
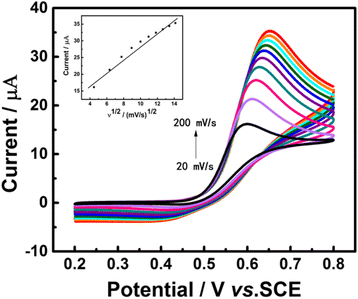
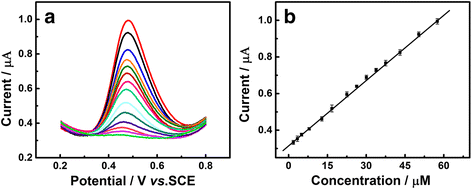
In this work, a sensitive and novel method for determining uric acid (UA) has been developed, in which the glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was modified with electrodeposition Au nanoparticles and used to monitor the concentration of UA with the assistant of visible light illumination. The morphology of the Au nanoparticles deposited on GCE surface were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and the nanoparticles were found to be well-dispersed spheres with the average diameter approaching 26.1 nm. A series of cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) measurements have revealed that the introduction of visible light can greatly enhance both the strength and stability of response current due to the surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Specifically, the DPV showed a linear relationship between peak current and UA concentration in the range of 2.8 to 57.5 μM with the equation of I pa (μA) = 0.0121c UA (μM) + 0.3122 (R 2 = 0.9987). Herein, the visible light illuminated Au/GCE possesses a potential to be a sensitive electrochemical sensor in the future.
Keywords: AuNPs; Uric acid; Visible light.
Conflict of interest statement
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Dai X, Fang X, Zhang C, Xu R, Xu B. Determination of serum uric acid using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)/isotope dilution mass spectrometry (ID-MS) as a candidate reference method. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007;857(2):287–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.07.035. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

