Microbiome Associated with Severe Caries in Canadian First Nations Children
- PMID: 28709393
- PMCID: PMC5652857
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034517718819
Microbiome Associated with Severe Caries in Canadian First Nations Children
Abstract
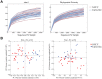
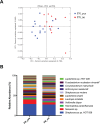
Young Indigenous children in North America suffer from a higher degree of severe early childhood caries (S-ECC) than the general population, leading to speculation that the etiology and characteristics of the disease may be distinct in this population. To address this knowledge gap, we conducted the first microbiome analysis of an Indigenous population using modern molecular techniques. We investigated the caries-associated microbiome among Canadian First Nations children with S-ECC. Thirty First Nations children <72 mo of age with S-ECC and 20 caries-free children were recruited in Winnipeg, Canada. Parents or caregivers completed a questionnaire on general and dental health, diet, and demographics. The plaque microbiome was investigated by sequencing the 16S rRNA gene. Sequences were clustered into operational taxonomic units and taxonomy assigned via the Human Oral Microbiome Database, then analyzed at the community level with alpha and beta diversity measures. Compared with those who were caries free, children with S-ECC came from households with lower income; they were more likely to live in First Nations communities and were more likely to be bottle-fed; and they were weaned from the bottle at a later age. The microbial communities of the S-ECC and caries-free groups did not differ in terms of species richness or phylogenetic diversity. Beta diversity analysis showed that the samples significantly clustered into groups based on caries status. Twenty-eight species-level operational taxonomic units were significantly different between the groups, including Veillonella HOT 780 and Porphyromonas HOT 284, which were 4.6- and 9-fold higher, respectively, in the S-ECC group, and Streptococcus gordonii and Streptococcus sanguinis, which were 5- and 2-fold higher, respectively, in the caries-free group. Extremely high levels of Streptococcus mutans were detected in the S-ECC group. Overall, First Nations children with S-ECC have a significantly different plaque microbiome than their caries-free counterparts, with the S-ECC group containing higher levels of known cariogenic organisms.
Keywords: Indigenous population; Streptococcus mutans; dental health survey; healthcare disparities; oral health; preschool child.
Conflict of interest statement
W. Shi is the founding scientist for C3 Jian, Inc., which has licensed anti–
Figures

References
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics. 2016. Policy on early childhood caries (ECC): classifications, consequences, and preventive strategies. Pediatr Dent. 38(6):52–54. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Native American Child Health and Canadian Paediatric Society First Nations, Inuit and Métis Committee. 2011. Early childhood caries in Indigenous communities. Pediatrics. 127(6):1190–1198. - PubMed
-
- Belstrøm D, Fiehn NE, Nielsen CH, Holmstrup P, Kirkby N, Klepac-Ceraj V, Paster BJ, Twetman S. 2014. Altered bacterial profiles in saliva from adults with caries lesions: a case-cohort study. Caries Res. 48(5):368–375. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

