Targeting Fyn Kinase in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 28709498
- PMCID: PMC5729051
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.06.004
Targeting Fyn Kinase in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
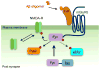
The past decade has brought tremendous progress in unraveling the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD). While increasingly sophisticated immunotherapy targeting soluble and aggregated brain amyloid-beta (Aβ) continues to dominate clinical research in AD, a deeper understanding of Aβ physiology has led to the recognition of distinct neuronal signaling pathways linking Aβ to synaptotoxicity and neurodegeneration and to new targets for therapeutic intervention. Identifying specific signaling pathways involving Aβ has allowed for the development of more precise therapeutic interventions targeting the most relevant molecular mechanisms leading to AD. In this review, I highlight the discovery of cellular prion protein as a high-affinity receptor for Aβ oligomers, and the downstream signaling pathway elucidated to date, converging on nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Fyn. I discuss preclinical studies targeting Fyn as a therapeutic intervention in AD and our recent experience with the safety, tolerability, and cerebrospinal fluid penetration of the Src family kinase inhibitor saracatinib in patients with AD. Fyn is an attractive target for AD therapeutics, not only based on its activation by Aβ via cellular prion protein but also due to its known interaction with tau, uniquely linking the two key pathologies in AD. Fyn is also a challenging target, with broad expression throughout the body and significant homology with other members of the Src family kinases, which may lead to unintended off-target effects. A phase 2a proof-of-concept clinical trial in patients with AD is currently under way, providing critical first data on the potential effectiveness of targeting Fyn in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid-beta; Cellular prion protein; Fyn; Saracatinib.
Copyright © 2017 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fyn Kinase in Alzheimer's Disease: Unraveling Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jan;62(1):643-660. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04286-2. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38890236 Review.
-
Current Research Therapeutic Strategies for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:8501693. doi: 10.1155/2016/8501693. Epub 2016 Jan 3. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 26881137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloid-β induced signaling by cellular prion protein and Fyn kinase in Alzheimer disease.Prion. 2013 Jan-Feb;7(1):37-41. doi: 10.4161/pri.22212. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Prion. 2013. PMID: 22987042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fyn inhibition rescues established memory and synapse loss in Alzheimer mice.Ann Neurol. 2015 Jun;77(6):953-71. doi: 10.1002/ana.24394. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Ann Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25707991 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's amyloid-β oligomers rescue cellular prion protein induced tau reduction via the Fyn pathway.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Sep 18;4(9):1287-96. doi: 10.1021/cn400085q. Epub 2013 Jul 18. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23805846 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic profiling of sporadic Alzheimer's disease patients.Mol Brain. 2022 Oct 12;15(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13041-022-00963-2. Mol Brain. 2022. PMID: 36224601 Free PMC article.
-
Fyn Kinase-Mediated PKCδ Y311 Phosphorylation Induces Dopaminergic Degeneration in Cell Culture and Animal Models: Implications for the Identification of a New Pharmacological Target for Parkinson's Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 28;12:631375. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.631375. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33995031 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of the juvenile form of Batten disease: important role of MAPK signaling pathways (ERK1/ERK2, JNK and p38) in pathogenesis of the malady.Biol Direct. 2018 Sep 25;13(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13062-018-0212-y. Biol Direct. 2018. PMID: 30621751 Free PMC article.
-
Tauopathy: A common mechanism for neurodegeneration and brain aging.Mech Ageing Dev. 2019 Mar;178:72-79. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2019.01.007. Epub 2019 Jan 19. Mech Ageing Dev. 2019. PMID: 30668956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-214 targets PTK6 to inhibit tumorigenic potential and increase drug sensitivity of prostate cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 5;9(1):9776. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46170-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31278310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer's A. 2016 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;12:459–509. - PubMed
-
- Nygaard HB. Current and emerging therapies for Alzheimer's disease. Clinical therapeutics. 2013;35:1480–1489. - PubMed
-
- Doody RS, Thomas RG, Farlow M, Iwatsubo T, Vellas B, Joffe S, et al. Phase 3 trials of solanezumab for mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease. The New England journal of medicine. 2014;370:311–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

