Ilioinguinal approach versus Stoppa approach for open reduction and internal fixation in the treatment of displaced acetabular fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28709737
- PMCID: PMC5555276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2017.01.005
Ilioinguinal approach versus Stoppa approach for open reduction and internal fixation in the treatment of displaced acetabular fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the efficacy and safety of open reduction and internal fixation through ilioinguinal approach and Stoppa approach for the treatment of displaced acetabular fractures.
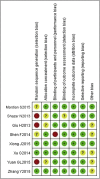
Methods: Case-controlled trials (CCTs) published from January 2010 to August 2015 that compared the ilioinguinal approach and Stoppa approach in the management of displaced acetabular fractures were retrieved from the databases of Cochrane Library, Pubmed, CNKI, and so on. Methodological quality of the trials was critically assessed. Statistical software RevMan 5.0 was used for data analysis.
Results: Eight articles were included in the meta-analysis. Through comparing the efficacy and safety of ilioinguinal approach and Stoppa approach in the treatment of displaced acetabular fracture, statistical significance was found in the average operation time [WMD = 68.29, 95% CI (10.52, 126.05), p < 0.05] and the median intraoperative blood loss [WMD = 142.26, 95% CI (9.30, 275.23), p < 0.05]. However, there existed no statistical significance in the fracture end reset satisfaction rate [RR = 0.63, 95% CI (0.17, 2.37), p > 0.05], the early complications rate [RR = 0.89, 95% CI (0.33, 2.40), p > 0.05], the late complications rate [RR = 0.91, 95% CI (0.27, 3.01), p > 0.05], and Harris hip score good function rate [RR = 0.52, 95% CI (0.25, 1.10), p > 0.05].
Conclusion: Though both techniques can obtain satisfactory clinical functions in the treatment of displaced acetabular fractures, Stoppa approach is superior to the ilioinguinal approach in terms of operation time and intraoperative blood loss.
Keywords: Displaced acetabular fractures; Ilioinguinal approach; Meta-analysis; Stoppa approach.
Copyright © 2017. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

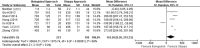
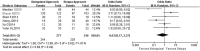
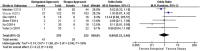




References
-
- Salama W., Mousa S., Khalefa A. Simultaneous open reduction and internal fixation and total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of steoporotic acetabular fractures. Int Orthop. 2017;41:181–189. - PubMed
-
- Peng Y., Zhang L., Min W. Comparison of anterograde versus retrograde percutaneous screw fixation of anterior column acetabular fractures. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2016;11:635–639. - PubMed
-
- Giannoudis P.V., Grotz M.R., Papakostidis C. Operative treatment of displaced fractures of the acetabulum. A meta-analysis. J Bone Jt Surg Br. 2005;87:2–9. - PubMed
-
- Chaus G.W., Heng M., Smith R.M. Occult internal iliac arterial injury identified during open reduction internal fixation of an acetabular fracture: a report of two cases. Injury. 2015;46:1417–1422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
