Interindividual Variability in Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Health after Consumption of Major Plant-Food Bioactive Compounds and the Determinants Involved
- PMID: 28710143
- PMCID: PMC5502866
- DOI: 10.3945/an.116.013623
Interindividual Variability in Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Health after Consumption of Major Plant-Food Bioactive Compounds and the Determinants Involved
Abstract
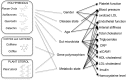
Cardiometabolic disease, comprising cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and their associated risk factors including metabolic syndrome and obesity, is the leading cause of death worldwide. Plant foods are rich sources of different groups of bioactive compounds, which might not be essential throughout life but promote health and well-being by reducing the risk of age-related chronic diseases. However, heterogeneity in the responsiveness to bioactive compounds can obscure associations between their intakes and health outcomes, resulting in the hiding of health benefits for specific population groups and thereby limiting our knowledge of the exact role of the different bioactive compounds for health. The heterogeneity in response suggests that some individuals may benefit more than others from the health effects of these bioactive compounds. However, to date, this interindividual variation after habitual intake of plant bioactive compounds has been little explored. The aim of this review is to provide an overview of the existing research that has revealed interindividual variability in the responsiveness to plant-food bioactive compound consumption regarding cardiometabolic outcomes, focusing on polyphenols, caffeine and plant sterols, and the identified potential determinants involved.
Keywords: biological responsiveness; cardiometabolic health; determinants of interindividual variability; interindividual variability; plant-food bioactives.
© 2017 American Society for Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures: DM, CM, AC, AK-R, FT-B, JMO, PK, RDC, and AR-M, no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Castro JP, El-Atat FA, McFarlane SI, Aneja A, Sowers JR. Cardiometabolic syndrome: pathophysiology and treatment. Curr Hypertens Rep 2003;5:393–401. - PubMed
-
- Ezzati M, Riboli E. Behavioral and dietary risk factors for noncommunicable diseases. N Engl J Med 2013;369:954–64. - PubMed
-
- Holst B, Williamson G. Nutrients and phytochemicals: from bioavailability to bioefficacy beyond antioxidants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2008;19:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Manach C, Scalbert A, Morand C, Remesy C, Jimenez L. Polyphenols: food sources and bioavailability. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;79:727–47. - PubMed