Protocol for regional implementation of community-based collaborative management of complex chronic patients
- PMID: 28710482
- PMCID: PMC5511202
- DOI: 10.1038/s41533-017-0043-9
Protocol for regional implementation of community-based collaborative management of complex chronic patients
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
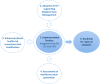
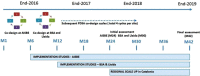



References
-
- Council conclusions “Innovative approaches for chronic diseases in public health and healthcare systems”. Council of the European Union 3053rd Employment. Social Policy Health and Consumer Affairs Council Meeting, Brussels. http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/lsa/118... (2010).
-
- Innovative Care for Chronic Conditions: Building Blocks for Action. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO/MNC/CCH/02.01). http://www.who.int/chp/knowledge/publications/icccreport/en/ (2002).
-
- Goodwin, N., Dixon, A., Anderson, G. & Wodchis, W. Providing integrated care for older people with complex needs: lessons from seven international case studies. Kings Fund. https://www.kingsfund.org.uk/sites/files/kf/field/field_publication_file... (2014). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

