Recent Advances on Nutrition in Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis
- PMID: 28713382
- PMCID: PMC5491641
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00762
Recent Advances on Nutrition in Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Recent Advances on Nutrition in Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 23;9:849. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00849. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29719542 Free PMC article.
Abstract
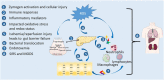
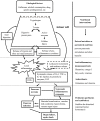
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a common abdominal acute inflammatory disorder and the leading cause of hospital admission for gastrointestinal disorders in many countries. Clinical manifestations of AP vary from self-limiting local inflammation to devastating systemic pathological conditions causing significant morbidity and mortality. To date, despite extensive efforts in translating promising experimental therapeutic targets in clinical trials, disease-specific effective remedy remains obscure, and supportive care has still been the primary treatment for this disease. Emerging evidence, in light of the current state of pathophysiology of AP, has highlighted that strategic initiation of nutrition with appropriate nutrient supplementation are key to limit local inflammation and to prevent or manage AP-associated complications. The current review focuses on recent advances on nutritional interventions including enteral versus parenteral nutrition strategies, and nutritional supplements such as probiotics, glutamine, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins in clinical AP, hoping to advance current knowledge and practice related to nutrition and nutritional supplements in clinical management of AP.
Keywords: amino acids; clinical management of acute pancreatitis; nutritional interventions; omega-3 fatty acids; prebiotics; probiotics; vitamins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutrition management in acute pancreatitis: Clinical practice consideration.World J Clin Cases. 2020 May 6;8(9):1561-1573. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i9.1561. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 32432134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional support in acute pancreatitis.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008 May;11(3):261-6. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3282fba5b4. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008. PMID: 18403922 Review.
-
Nutritional management of acute pancreatitis in dogs and cats.J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2014 May-Jun;24(3):240-50. doi: 10.1111/vec.12180. Epub 2014 Apr 1. J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2014. PMID: 24690138 Review.
-
Nutritional Management of Acute Pancreatitis.Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2021 Mar;50(1):141-150. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2020.10.014. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2021. PMID: 33518160 Review.
-
[Guidelines for specialized nutritional and metabolic support in the critically ill-patient. Update. Consensus of the Spanish Society of Intensive Care Medicine and Coronary Units-Spanish Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (SEMICYUC-SENPE): severe acute pancreatitis].Med Intensiva. 2011 Nov;35 Suppl 1:33-7. doi: 10.1016/S0210-5691(11)70007-9. Med Intensiva. 2011. PMID: 22309750 Spanish.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiome in acute pancreatitis: A review based on current literature.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Aug 14;27(30):5019-5036. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.5019. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34497432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Fibre in Nutritional Management of Pancreatic Diseases.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 14;11(9):2219. doi: 10.3390/nu11092219. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31540004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated Serum miR-7, miR-9, miR-122, and miR-141 Are Noninvasive Biomarkers of Acute Pancreatitis.Dis Markers. 2017;2017:7293459. doi: 10.1155/2017/7293459. Epub 2017 Dec 3. Dis Markers. 2017. PMID: 29332987 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics, their prophylactic and therapeutic applications in human health development: A review of the literature.Heliyon. 2022 Jun 22;8(6):e09725. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09725. eCollection 2022 Jun. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35785237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Butyrate ameliorates caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis and associated intestinal injury by tissue-specific mechanisms.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Dec;176(23):4446-4461. doi: 10.1111/bph.14806. Epub 2019 Dec 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31347703 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

