Abducent nerve palsy after microballoon compression of the trigeminal ganglion: Case report
- PMID: 28713629
- PMCID: PMC5502296
- DOI: 10.4103/sni.sni_375_16
Abducent nerve palsy after microballoon compression of the trigeminal ganglion: Case report
Abstract
Background: Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is the most common type of facial neuralgia with incidence of 26.8/100,000 person year. In general, this scenario is characterized by a lancinating, unilateral, paroxysmal pain in the area of the fifth cranial nerve. Several treatment methods, including the injection of ethyl alcohol or butyl alcohol into the ganglion, the glycerol injection into the trigeminal cistern, peripheral nerve divisions, the radiofrequency thermocoagulation of the preganglionic fibers, and radiosurgery has been used for TN.
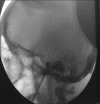
Case description: A case of a 74-year-old woman patient who undergone a treatment of TN through a compression of Meckel cave and developed a transient abducent palsy is presented. Complication regarding to a palsy of abducent nerve is discussed as well as the analysis of presumable evolving physiopathology. A critical review of literature was performed.
Conclusions: Among the procedures, we mean that percutaneous microballoon compression (PMC) is the best choice for elderly frail patients, because it had a very low associated mortality-morbidity rate and does not damage permanent the Gasserian ganglion.
Keywords: Abducent palsy; Gasserian ganglion; balloon compression; diplopia; percutaneous procedures; trigeminal neuralgia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bergenheim AT, Linderoth B. Diplopia after balloon compression of retrogasserian ganglion rootlets for trigeminal neuralgia: Technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2008;62:E533–4. - PubMed
-
- Brown JA, Chittum CJ, Sabol D, Gouda JJ. Percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal nerve for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Focus. 1996;1:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Brown JA, Gouda JJ. Percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal nerve. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1997;8:53–62. - PubMed
-
- Brown JA, McDaniel MD, Weaver MT. Percutaneous trigeminal nerve compression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: Results in 50 patients. Neurosurgery. 1993;32:570–3. - PubMed
-
- Brown JA, Pilitsis JG. Percutaneous balloon compression for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: Results in 56 patients based on balloon compression pressure monitoring. Neurosurg Focus. 2005;18:E10. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources