Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension
- PMID: 28713844
- PMCID: PMC5506688
- DOI: 10.1002/mdc3.12478
Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension
Abstract
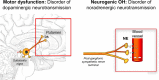
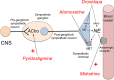
Background: Orthostatic hypotension (OH) is a sustained fall in blood pressure on standing which can cause symptoms of organ hypoperfusion. OH is associated with increased morbidity and mortality and leads to a significant number of hospital admissions particularly in the elderly (233 per 100,000 patients over 75 years of age in the US). OH can be due to volume depletion, blood loss, large varicose veins, medications, or due to defective activation of sympathetic nerves and reduced norepinephrine release upon standing (i.e., neurogenic OH).
Methods and findings: Literature review. Neurogenic OH is a frequent and disabling problem in patients with synucleinopathies such as Parkinson disease, multiple system atrophy, and pure autonomic failure, and is commonly associated with supine hypertension. Several pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapeutic options are available.
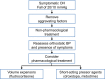
Conclusions: Here we review the epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of neurogenic OH, and provide an algorithm for its treatment emphasizing the importance of removing aggravating factors, implementing non-pharmacologic measures, and selecting appropriate pharmacological treatments.
Keywords: Autonomic failure; Droxidopa; Multiple system atrophy; Parkinson disease; Supine hypertension; Synucleinopathies.
Figures

References
-
- Freeman R, Wieling W, Axelrod FB, et al. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Auton Res 2011;21:69–72. - PubMed
-
- Freeman R. Clinical practice: neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med 2008;358:615–624. - PubMed
-
- Masaki KH, Schatz IJ, Burchfiel CM, et al. Orthostatic hypotension predicts mortality in elderly men: the Honolulu Heart Program. Circulation 1998;98:2290–2295. - PubMed
-
- Arenander E. Hemodynamic effects of varicose veins and results of radical surgery. Acta Chir Scand Suppl 1960; 260 Suppl :1–76. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann H, Biaggioni I. Autonomic failure in neurodegenerative disorders. Semin Neurol 2003;23:351–363. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

