Tofacitinib for the treatment of moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis in Japanese patients: Subgroup analyses from a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial
- PMID: 28714180
- PMCID: PMC5697670
- DOI: 10.1111/1346-8138.13956
Tofacitinib for the treatment of moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis in Japanese patients: Subgroup analyses from a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial
Abstract
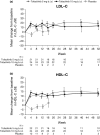
Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor. These post-hoc analyses assessed tofacitinib efficacy and safety in Japanese patients with psoriasis enrolled in a 52-week global phase 3 study. Patients received tofacitinib 5 mg, tofacitinib 10 mg or placebo twice daily (b.i.d.); placebo-treated patients advanced to tofacitinib at week 16. Primary efficacy end-points were the proportions of patients with 75% or more reduction from baseline Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI-75) and Physician's Global Assessment (PGA) of "clear" or "almost clear" (PGA response) at week 16. Other end-points included: Itch Severity Item (ISI), Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) score and Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (NAPSI). Adverse events (AEs) were recorded throughout the study. Overall, 58 Japanese patients were included in this analysis (tofacitinib 5 mg b.i.d., n = 22; 10 mg b.i.d., n = 24; placebo, n = 12); 29 completed the study. At week 16, significantly more patients receiving tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg b.i.d. versus placebo achieved PASI-75 (50% and 75% vs 0%, P < 0.01) and PGA response (59% and 75% vs 0%, P < 0.001). Substantial improvements in ISI, DLQI and NAPSI score were observed with both tofacitinib doses. Over 52 weeks, similar rates of AEs were reported across treatment groups; one serious AE occurred with tofacitinib 10 mg b.i.d. Herpes zoster occurred in three patients receiving tofacitinib 10 mg b.i.d. No deaths, serious infections, malignancies or gastrointestinal perforations were reported. Results were generally consistent with global analysis, suggesting sustained efficacy and a manageable safety profile, with increased herpes zoster incidence, of tofacitinib in Japanese patients with psoriasis.
Keywords: Janus kinase inhibitor; Japanese; oral medicine; plaque psoriasis; tofacitinib.
© 2017 The Authors. The Journal of Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Dermatological Association.
Figures


References
-
- Boehncke WH, Schon MP. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015; 386: 983–994. - PubMed
-
- Cohen AD, Dreiher J, Shapiro Y et al Psoriasis and diabetes: a population‐based cross‐sectional study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2008; 22: 585–589. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro J, Cohen AD, Weitzman D, Tal R, David M. Psoriasis and cardiovascular risk factors: a case‐control study on inpatients comparing psoriasis to dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2012; 66: 252–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

