Physical Outdoor Activity versus Indoor Activity: Their Influence on Environmental Behaviors
- PMID: 28714934
- PMCID: PMC5551235
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph14070797
Physical Outdoor Activity versus Indoor Activity: Their Influence on Environmental Behaviors
Abstract
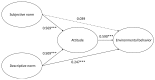
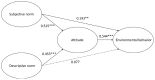
There are strong evidences linking physical outdoor activity and health benefits; however, little is known about the impact on environmental behaviors. Thus, this study aims to close this gap by investigating the influence of physical outdoor activity on environmental behaviors. A total of 416 surveys were distributed to students in eight public primary schools located near the Hsinchu Science and Industrial Park in Taiwan. Findings from the analysis revealed that subjective norms had a more influential effect on environmental behaviors for participants who engaged in physical activity at outdoor parks. In contrast, descriptive norms had a direct predictive impact on environmental behaviors for participants whose main physical activity venue was at the indoor after-school centers. Research results also highlighted attitude as the strongest predictive variable influence on environmental behaviors for children who engaged in physical indoor and outdoor activities.
Keywords: environmental behaviors; physical outdoor activity; primary school children; social norms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cheng J.C.-H., Monroe M.C. Connection to nature children’s affective attitude toward nature. Environ. Behav. 2012;44:31–49. doi: 10.1177/0013916510385082. - DOI
-
- Koger S.M., Winter D.D. The Psychology of Environmental Problems: Psychology for Sustainability. 3rd ed. Psychology Press; New York, NY, USA: 2011.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous