Tales of diversity: Genomic and morphological characteristics of forty-six Arthrobacter phages
- PMID: 28715480
- PMCID: PMC5513430
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180517
Tales of diversity: Genomic and morphological characteristics of forty-six Arthrobacter phages
Abstract
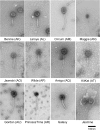
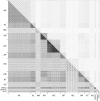
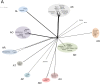
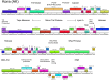
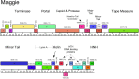
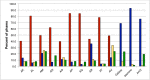
The vast bacteriophage population harbors an immense reservoir of genetic information. Almost 2000 phage genomes have been sequenced from phages infecting hosts in the phylum Actinobacteria, and analysis of these genomes reveals substantial diversity, pervasive mosaicism, and novel mechanisms for phage replication and lysogeny. Here, we describe the isolation and genomic characterization of 46 phages from environmental samples at various geographic locations in the U.S. infecting a single Arthrobacter sp. strain. These phages include representatives of all three virion morphologies, and Jasmine is the first sequenced podovirus of an actinobacterial host. The phages also span considerable sequence diversity, and can be grouped into 10 clusters according to their nucleotide diversity, and two singletons each with no close relatives. However, the clusters/singletons appear to be genomically well separated from each other, and relatively few genes are shared between clusters. Genome size varies from among the smallest of siphoviral phages (15,319 bp) to over 70 kbp, and G+C contents range from 45-68%, compared to 63.4% for the host genome. Although temperate phages are common among other actinobacterial hosts, these Arthrobacter phages are primarily lytic, and only the singleton Galaxy is likely temperate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures












References
-
- Hendrix RW. Bacteriophages: evolution of the majority. Theor Popul Biol. 2002;61(4):471–80. . - PubMed
-
- Benson DA, Clark K, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Sayers EW. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D32–7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1030 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3965104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dyson ZA, Tucci J, Seviour RJ, Petrovski S. Lysis to Kill: Evaluation of the Lytic Abilities, and Genomics of Nine Bacteriophages Infective for Gordonia spp. and Their Potential Use in Activated Sludge Foam Biocontrol. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0134512 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134512 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4524720. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu M, Gill JJ, Young R, Summer EJ. Bacteriophages of wastewater foaming-associated filamentous Gordonia reduce host levels in raw activated sludge. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13754 doi: 10.1038/srep13754 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4563357. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khairnar K, Pal P, Chandekar RH, Paunikar WN. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages infecting nocardioforms in wastewater treatment plant. Biotechnol Res Int. 2014;2014:151952 doi: 10.1155/2014/151952 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4129933. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

